Clinical Case Reports and Clinical Study
OPEN ACCESS | Volume 13 - Issue 1 - 2026
ISSN No: 2766-8614 | Journal DOI: 10.61148/2766-8614/JCCRCS
Takaki Shimura1*, Eriko Okuyama2, Atsuko Suzuki1 and Hironori Ohsugi3
1BME Research Lab. Sosei Ltd., Japan
2Hamamatsu Human Research Lab. Ltd., Japan
3Josai International University,Japan
*Corresponding Author: Takaki Shimura, BME Research Lab. Sosei Ltd., Japan.
Received: September 11, 2022
Accepted: September 16, 2022
Published: September 20, 2022
Citation: Takaki Shimura, Eriko Okuyama, Atsuko Suzuki and Hironori Ohsugi (2022) “Examining the Normality of 15-Year Large-Scale CKPT (Japanese Version of CWPT) Results”, Clinical Case Reports and Clinical Study, 5(7); DOI: http;//doi.org/09.2022/1.149.
Copyright: © 2022 Takaki Shimura. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly Cited.
Objective: Since 2006, Index1 obtained by CKPT which is a neuropsychological test that detects slight declines in brain function before dementia, have been accumulated. The basis for setting diagnostic criteria using Index1 is based on the fact that large-scale data of Index1are normally distributed. The purpose of this analysis is to test the normality of large-scale data accumulated over 15 years.
Methods: The accumulated large-scale data were first grouped by gender and 60s, 70s and 80s over the full period from 2006 to 2020, and the histogram normality test using Shapiro-Wilk was performed for each. Next, the period was divided into 2006-2010, 2011-2015 and 2016-2020 and similar tests were performed. The total number of subjects is 2555.
Results:
In the full-period test, only female in their 60s, 70s, and 80s were found to be non-normal. Normality was confirmed for all groups in the 5-year interval test.
Consideration and Summery:
In 1945, Japan underwent a major transformation from Emperor's Absolutism to Democracy. It is believed that this was a shock to the development of the frontal lobes of children aged 6-8, who were in the lower grades of elementary school at the time. I believe this may be one reason why the full-period histogram did not follow a normal distribution. In order to pursue the impact of this shock, it is necessary to examine the analysis period more strictly. This survey suggests that the large-scale data collection period for deriving the diagnostic reference value should be about 5 years in Japan.
Background
Fig. 1 illustrates the progression of degenerative types of dementia and the scope of application of CKPT. In the figure, the progression of cognitive impairment is shown from left to right, and the preclinical stage is an institution where cognitive impairment does not appear for 10 to 20 years when neurotransmission inhibitors are deposited1-2). Recently, research on dementia has shifted to the preclinical stage and MCI3), and there is a need for an economical method to determine the effects of both drug therapy and non-drug therapy. Molecular imaging methods such as PET which are available for diagnoses in the preclinical stage require exposure to radiation and high imaging costs, and do not meet this requirement. We have been focusing on neuropsychological tests that can be examined in groups.
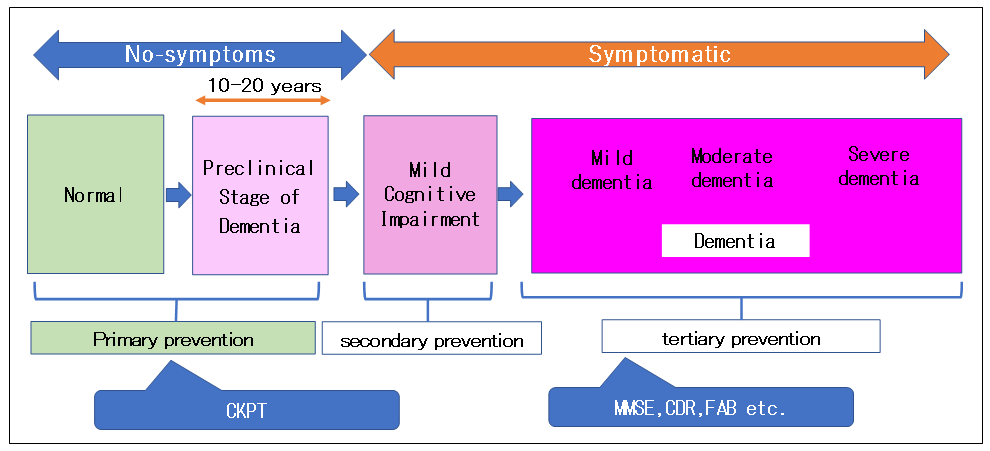
Fig.1 Progression of degenerative type of dementia
Neuropsychological tests such as MMSE4) and CDR5), are tests applied after the onset of dementia. If they are applied before the onset of dementia, the histogram will be biased toward high scores as shown in Fig. 2(a), and classification cannot be performed. On the other hand, since CKPT histogram has a normal distribution, it is characteristic that it can be easily classified into classes using the mean and standard deviation in Fig.2(b).
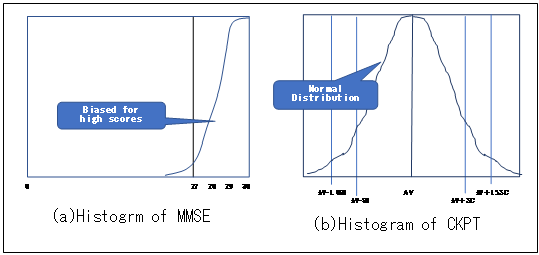
Fig.2 Comparison of histogram of MMSE and CKPT
CWPT was devised in 20036), and evidence has been established using CKPT7) which is the Japanese version of CWPT, and diagnostic criteria have been established using large-scale data8). After that, the test was conducted on 1,325 subjects who said, "I don't have dementia" and "I don't want to fall into dementia." It has been founded that as the age increases, the rate of the people who are judged as abnormal increases8). An overview of CKPT is provided in the appendix of this paper.
Objective
Since 2006, data of Index1 obtained by CKPT, a neuropsychological test that detects slight declines in brain function before dementia, have been accumulated. The basis for setting diagnostic criteria using Index1 is based on the fact that large-scale CKPT data are normally distributed. The purpose of this analysis is to test the normality of large-scale data accumulated over 15 years.
Methods
Analysis of the entire period
Table 1 shows the subjects used in the analysis for the entire period (2006-2020). Shapiro-Wilk examination was used for normality testing.
Table 1 Subjects of the entire period (2006-2020)
|
Age |
Gender |
Number |
|
60's |
Male |
351 |
|
Female |
880 |
|
|
70's |
Male |
283 |
|
Female |
821 |
|
|
80's |
Male |
72 |
|
Female |
148 |
|
|
Total |
2555 |
|
Analysis of the split period
The period was divided into 2006-2010, 2011-2015, and 2016-2020, and similar examinations as analysis of the entire period were performed. Table2-4 show the subjects in each period.
Table 2 Subjects of the split period (2006-2010)
|
2006-2010 |
||
|
Age |
Gender |
Number |
|
60's |
Male |
127 |
|
Female |
433 |
|
|
70's |
Male |
109 |
|
Female |
357 |
|
|
80's |
Male |
34 |
|
Female |
67 |
|
Table 3 Subjects of the split period (2011-2015)
|
2011-2015 |
||
|
Age |
Gender |
Number |
|
60's |
Male |
167 |
|
Female |
337 |
|
|
70's |
Male |
121 |
|
Female |
333 |
|
|
80's |
Male |
29 |
|
Female |
64 |
|
Table 4 Subjects of the split period (2016-2020)
|
2016-2020 |
||
|
60's |
Male |
57 |
|
Female |
110 |
|
|
70's |
Male |
53 |
|
Female |
131 |
|
|
80's |
Male |
9 |
|
Female |
17 |
|
Results
Analysis of the entire period
Table 5 shows Shapiro-Wilk test results obtained by analysis of the entire period. If the probability of significance is 0.05 or more, the null hypothesis that the histogram has normality is not denied, so it is tested as a normal distribution. All of female in their 60s, 70s, and 80s were found to be non-normal distribution, whereas all of male showed normal distribution for all age groups.
Table 5 Analysis of the entire period
|
Shapiro-Wilk |
||||
|
Age |
Gender |
Statistics |
Degrees of freedom |
Significance |
|
60's |
Male |
.992 |
351 |
.053 |
|
Female |
.995 |
880 |
.011 |
|
|
70's |
Male |
.993 |
283 |
.208 |
|
Female |
.995 |
821 |
.005 |
|
|
80's |
Male |
.971 |
72 |
.095 |
|
Female |
.981 |
148 |
.034 |
|
Analysis of the split period
The results are shown in Table6. Please confirm that the probability of significance is 0.05 or more. Therefore, all of the distribution of histogram are proved to be normal distribution.
Table 6 Analysis of the split period
|
|
|
Shapiro-Wilk |
||||
|
Period |
Ages |
Gender |
|
Statistics |
Degrees of freedom |
Significance |
|
2006-2010 |
60's |
Male |
|
.988 |
127 |
.307 |
|
Female |
|
.994 |
433 |
.091 |
||
|
70's |
Male |
|
.985 |
109 |
.255 |
|
|
Female |
|
.993 |
357 |
.117 |
||
|
80's |
Male |
|
.981 |
34 |
.791 |
|
|
Female |
|
.970 |
67 |
.107 |
||
|
2011-2015 |
60's |
Male |
|
.987 |
167 |
.109 |
|
Female |
|
.994 |
337 |
.225 |
||
|
70's |
Male |
|
.983 |
121 |
.125 |
|
|
Female |
|
.992 |
333 |
.081 |
||
|
80's |
Male |
|
.939 |
29 |
.092 |
|
|
Female |
|
.977 |
64 |
.275 |
||
|
2016-2020 |
60's |
Male |
|
.961 |
57 |
.066 |
|
Female |
|
.992 |
110 |
.783 |
||
|
70's |
Male |
|
.967 |
53 |
.152 |
|
|
Female |
|
.988 |
131 |
.339 |
||
|
80's |
Male |
|
.947 |
9 |
.660 |
|
|
Female |
|
.916 |
17 |
.124 |
||
Considerations
The diagnostic criteria for CKPT presuppose that the histogram has a normal distribution, and the accuracy of the diagnostic criteria increases as the amount of collected data increases. For this reason, we examined how long the period is allowed.
(1) From the test results of all data from 2006 to 2020, male in their 60s, 70s, and 80s showed a normal distribution, whereas female in all ages did not show a normal distribution. It can be expected that the Japanese national polity in 1945 was excessively changed from Emperor's Absolutism to Democracy, and that the change affected the results. Further examination is necessary to prove this.
(2) When the periods were divided into five-year periods, the normality of the histograms was verified for all cases by gender and age group. It was suggested that accumulation of Index 1 for 5 years is allowed in Japan.
Summery
The basis for setting diagnostic criteria using Index1 obtained by CKPT is based on the fact that large-scale Index1 data are normally distributed. Since the reference value for diagnosis is derived for each sex and age group, it is important whether the histogram for each sex and age group has a normal distribution. The normality of histograms was examined. All data from 2006-2020 found no normality in histograms for female in their 60s, 70s, and 80s. However, the histogram of male showed to be normal. On the other hand, the result of testing the normality in 5-year increments, that is, 2006-2010, 2011-2015, and 2016-2020, showed that the histograms of all ages for both male and female had a normal distribution. In summary, it was suggested that in Japan, diagnostic criteria can be established using large-scale data accumulated over a period of 5 years.
The test can be easily translated into other languages, so it has potential for international expansion. The English translated version has already been prepared10), so please contact me if you are interested. E-mail: tshimura@tuba.ocn.ne.jp.
Appendix:CKPT
In CKPT, a story including color words are shown first like Fig.A1. Subjects should read the story memorizing the episode of it, and simultaneously pick-out color words discerning the matching of meaning and printed color of them. After a certain period of time, the subjects stop the task of determining the color words of Story, and answer Questions (Fig,A2) regarding the episode memorized without seeing Story. CKPT is the most advanced neuro-psychological test which is an application of Stroop EffectA1), with a short-term memory function examination.

Fig.A1 A sample of Story of CKPT

Fig.A2 A sample of Questions
Reference of Appendix
A1) Stroop JR: Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions, J Experimental Psychology 18: 643-662 (1935).