Clinical Case Reports and Clinical Study
OPEN ACCESS | Volume 13 - Issue 1 - 2026
ISSN No: 2766-8614 | Journal DOI: 10.61148/2766-8614/JCCRCS
Kulvinder Kochar Kaur 1*, Gautam Allahbadia 2 , Mandeep Singh 3
1 Scientific Director, Dr Kulvinder Kaur Centre For Human Reproduction 721,G.T.B. Nagar JALANDHAR-144001, PUNJAB,INDIA
2 Scientific Director, Ex-Rotunda-A Centre for Human reproduction 672,Kalpak Garden,Perry Cross Road, Near Otter’s Club,Bandra(W)-400040, MUMBAI,INDIA
3 Consultant Neurologist Swami Satyanand Hospital Near Nawi Kachehri,Baradri, Ladowali road,JALANDHAR, PUNJAB
*Corresponding author: Kulvinder Kochar Kaur, Scientific Director, Dr Kulvinder Kaur Centre For Human Reproduction 721,G.T.B. Nagar JALANDHAR-144001, PUNJAB,INDIA.
Received: February 08, 2021
Accepted: February 18, 2021
Published: February 22, 2021
Citation: Kulvinder K Kaur, Allahbadia G, Singh M. “An Update on Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Central Nervous System in health along with various diseases –implications in treating brain tumours as well-A Systematic Review”. Clinical Case Reports and Clinical Study, 2(2); DOI: 10.61148/2766-8614/JCCRCS/021
Copyright: © 2021 Kulvinder Kochar Kaur. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Matrix Metalloproteinases(MMP’s) represent zinc-endopeptidases possessing versatile actions in the human body both in health as well as disease.Earlier we reviewed the role of MMP’s in normal female reproductive system in health along with pregnancy as well as associated disorders .In the brain these MMP’s are key for tissue generation, neuronal network refashioning along with Blood Brain Barrier(BBB) integrity .Earlier reviews have concentrated only on 2 MMP’s namely MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 ,besides their part in one or few diseases.As our indepth understanding has grown with newer MMPs getting unraveled we decided to conduct a systematic review on MMPs in brain, BBB in neuroinflammation along with Central Nervous System( CNS) disease like multiple sclerosis(MS),cerebral aneurysm,stroke ,epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease(PD) ,Alzheimers disease(AD), along with brain cancer all related to neuroinflammation.Thus a systematic review was carried out using the pubmed and Google Scholar Search engine with the MeSH Terms; Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP’s) along with their inhibitors,namely the, Tissue inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinases(TIMP); MS; cerebral aneurysm,stroke ,epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease(PD) ,Alzheimers disease(AD); brain cancer;Newer MMP inhibitors ;other therapies related to thesefrom 1900 to date in January 2021.We found a total of 4500 articles out of which we selected 220 articles for this review.No meta-analysis was done .Here we detail the update on MMP’s as well as how they aid in neuroinflammation,barrier leakage neurotoxicity ,demyelination,tumor growth,angiogenesis as well as metastasis.Till date other than doxyxcycline or minocycline no MMP Inhibitor has been approved by the FDA for clinical use .Further how honey bee products might be aiding in manipulation of MMPs along with newer MMP Inhibitors have been studies in human status epilepticus and more indepth studies are going on Knowing the significance of extracellular vesicles (ECV’s) in various diseases NDEVS can be targeted for developing specific therapies as in tumours with ECV’s overexpressing certain miR’s .
1. Introduction
Matrix Metalloproteinases(MMP’s) MMP’s represent calcium -based zinc-endopeptidases that belong to the metzincin superfamily[1]. MMP possesses structurally a conserved Zn2+ -binding motif within the catalytic –domain along with various conserved protein domains (figure1)[2,reviewed in 3].
MMP’s get expressed in the form of inactive zymogens possessing a pro-peptide domain(pro- MMP’s),which need removal for the activation of MMP’s.This pro-peptide belongs to the portion of the ‘’cysteine switch’’.,that is an intra Molecular complex among a single cysteine in the pro-peptide domain along with zinc in the active site.Via cleavage of the pro-peptide, this cysteine separates from the complex ,that activates the MMP enzymes that aids binding along with cleavage of MMP substrates . MMPs further possess amino terminal signal sequence that guides the peptide towards the Endoplasmic reticulum(ER). Additionally, every MMP,but for MMP-7 along with MMP-26 possess a haemopexin –like domain which is connected to the catalytic – domain ,besides having the role in MMP’s Crosstalk with substrates,endogenous inhibitors, In addition to cell surface Molecules.
1.2 Discovery
Initial MMP(MMP1) got isolated by Gross as well as Lapierre in 1962 in tadpole [4].The 1st human MMP got discovered in skin tissue [5]. Subsequently ,a huge family of MMP’s got detailed in different species[1]. MMP’s got demonstrated to get bio generated in the form of bioactive precursors(zymogens) which needed activation[6].The initial inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinases, Tissue inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinases (TIMPs) ,got isolated in 1975 along with till date ,4 TIMPs(TIMP1-4) have got detailed [7].In 1990,the ‘’cysteine switch’’ MMP activation mode got identified [8]. Following, that our insight regarding MMP biology has escalated considerably .On finding of the MMP catalytic cycle, at present insight is there regarding the method by which MMP’s digest the extra cellular Matrix( ECM) proteins along with further aiding in fine tuning of the cellular events. Additionally, newer MMP’s - MMP-20 , MMP-206 as well as MMP-28-got isolated over the period of past 25 yrs[9].
1.3 Classification
Presently ,24 human MMP homologues have got detailed getting divided into 6 families
i)collagenases(MMP’s --1,-8 as well as -13) ii)gelatinases(MMP-2, as well as a-9iii)stromelysins (MMP-3,-10, as well as -11)iv)matrilysins (MMP -7 as well as -26)v) membrane type Metalloproteinases()MT1-MMP’s),also known as MMP-14,-15,-16,-17,-24, as well as -25) along with rest of MMP’s(MMP-12,18,-19,-20,-21,-22,-23,-27 as well as -28[10].
1.4 Actions of MMP’s
MMP’s possess a physiological part in tissue morphogenesis,cell migration along with angiogenesis.Besides that MMP’s are implicated in patho physiological events like wound healing , inflammation, as well as cancer .Certain posits that MMP’s cleave the extra cellular Matrix (ECM ) proteins to aid in infiltration of leukocytes,metastatic In addition to transformed cells to be able to go through the ECM barriers [11]. Nevertheless, there is controversy following the 1st in vitro study which correlated MMP’s with cleavage of the ECM Molecules that were dependent on experiments utilizing,enhanced levels of MMP’s in vivo[12].
Experiments utilizing mass spectrometry point that extra cellular Matrix (ECM) Molecules are MMP substrates as well as other studies demonstrated that blocking MMP’s(MT1-MMP’s) avoid leukocytes crossing the artificial collagen along with ECM layers[11,13].These studies illustrated that fibroblasts as well as tumor cells tunnel via the dense barriers of cross linked type-1 collagen in vitro or in vivo through a practically undistinguishable proteolytic event needing MMP’s ,.Moreover Ota etal., demonstrated that cancer cells use MT1 as well as MT2 based - MMP’s BM transmigration event for intravasation into the vasculature in vivo .
Separate work utilizing MMP knockout (KO) mice along with innovative mass spectrometry methods which aided in better tissue evaluation illustrated a broad MMP substrates spectrum like cell surface Molecules ,besides soluble factors like cytokines,chemokines as well as cytokine receptors [13]. Cleavage brought about of substrates via MMP,manipulated their activity along with being a significant mode for fine tuning of the cellular events like inflammation[13-15].Hence MMP s are key for refashioning events in generation as well as regeneration of tissues[11,13].
1.5 Expression, control as well as activation
Every MMP,other than MMP-28,are Expressed throught body in the mammalian organisms.Usually Expression, amounts remain while escalate only if and when required [16]other than MMP-2 as well as MT1-MMP,(besides to a lesser amount for –MMP-9,that are constitutively expressed in the brain in both their pro along with activated forms[17]. MMPs get formed along with liberated into the extra cellular space in an active latent pro-peptide form( zymogens),that gets activated via the proteolysis of the N-terminal pro- domain(figure1).This event aids in fast control of MMP activity ,hence regulates the cytokine as well as chemokine availability. Subsequently, MMP’s remain key in regulating rapid cellular events ,like cell migration at the time of inflammation.
In normal physiological situations,maximum MMP’s are activated by other MMP’s or proteases in the extra cellular spaces but certain MMP’s get activated intracellularly by the enzyme fibrin ,or via separate modes (like phosphorylation . MMP inhibition conversely gets modulated via Tissue inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinases (TIMPs),that are copresent with MMP’s[7,18]. TIMPs inactivate MMP action by binding to them,that in physiological situations avoid enhanced tissue breakdown along with injury .In pathophysiological events , activation of reactive oxygen species(ROS) along with separate factors(like Nitric oxide(NO),hypoxia ,pH)via a mode that probably implicates auto catalytic activation[19].
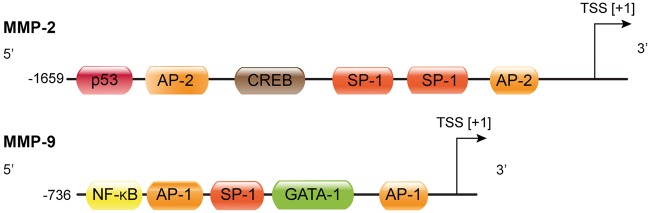
Regarding the transcriptional MMP control ,much knowledge does not exist ,just as for inflammatory signalling .Tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNF-α) along with interleukin -17(IL-17) are believed to stimulate transcription of via transcription factor activator protein-1(AP-1 ) along with nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB)[20,21].This action is blocked by interferon gamma via NFκB) inhibition[22]. Lipopolysaccharide(LPS) ,an endotoxin stimulates Reactive oxygen species(ROS ) generation along with p38 kinase phosphorylation,that activates AP-1 besides stimulation of MMP-9 transcription[23] . Infigure2 the MMP-9 promoter along with oneNuclear factor-κB immunoglobulin κ chain enhancer of B-cell (NFκB) along with 2 AP-1 binding sites are illustrated.Conversely MMP-2 is controlled by TNF-α as well as p38- MAPK, working via NFκB,but not AP-1(fig2),besides a caspase-8 based pathway CNS [24].In toto MMP control is not clear fully as well as differs among cell kinds along with context based manner[25].
Courtesy ref no-3-MMP-2 and MMP-9 promoter region with putative transcription factor binding sites. The boxes represent binding sites for the corresponding transcription factors. TSS: transcription start site; AP-1: activator protein 1; AP-2: activator protein 2; GATA-1: GATA-binding factor 1, erythroid transcription factor, globin transcription factor 1; SP-1: specificity protein 1; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB, CREB: cyclic AMP response-element binding protein; p53: tumor protein p53 (modified after Peters et al.38 and Rosenberg39).
1.6 MMP in brain along with Blood Brain Barrier
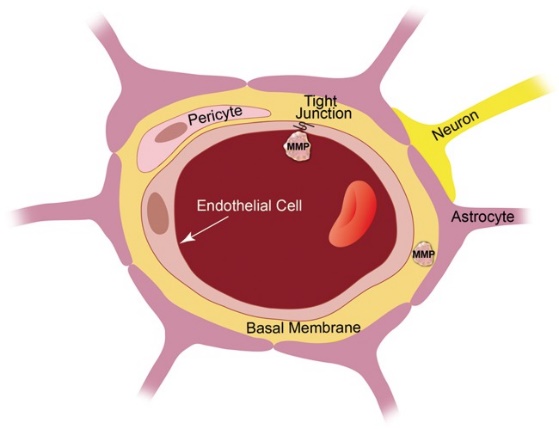
MMPs take part in a lot of physiological along with pathological events in the brain as well as Blood Brain Barrier (BBB).The BBB represents the capillary endothelium which partitions blood frombrain[26].This physical barrier function is present in 3 areas which are key regards to barrier integrity –i)the capillary endothelium of the Brain ii)tight junctions in between endothelial cells iii)basement membrane(BM)(Figure3)[26].
Courtesy ref no-3-Blood–brain barrier anatomy. The blood–brain barrier is formed by capillary endothelial cells that are linked by tight junctions, surrounded by a basement membrane, and astrocytic endfeet. Astrocytes provide the cellular link to neurons; pericytes are embedded in the basement membrane. In disease, MMP protein expression and activity levels are increased, which is thought to result in blood–brain barrier leakage, possibly through degradation of tight junction and basement membrane proteins.
i)the the capillary endothelium of the Brain becomes a barrier for small hydrophilic compounds.ii) tight junctions seals the openings in between the endothelial cells next to it ,that avoids the unregulated paracellular passing of solutes In addition to converting the endothelium of brain, a low permeability Barrier[27].The main tight junction proteins in the endothelium of Brain being claudin -1, claudin -5,occludin as well as zona occludens-1.iii)The (BM representing a specialized ECM,that bridges endothelial cells with the pericytes along with astrocytes to generate the neurovascular unit as well as promoting crosstalk among cells in this unit via receptors like integrins as well as dystroglycans[28].
Endothelial cells, tight junctions along with BM are key for appropriate Barrier function,subsequently for Brain homeostasis as well as total health of brain.Hence pathological impeachment of the endothelium, tight junctions along with BM,resulting in impairment of barrier integrity,that can cause marked problems for the Brain,resulting in disease propagation[29,30.It has been posited that MMP’s digest tight junctions along with BM proteins, hence being key in aiding towards brain disease along with directly influencing Brain health[31,32]. Nevertheless, minimal data is there to validate this in view of technical problems to show MMPactivity in vivo.Like Gu etal.,[33] demonstrated escalated MMPactivity as well as greater permeability at the BBB in stroke ,at the time of reperfusion in vivo. Escalated MMP2 as well as MMP-9mRNA along with activity levels following reperfusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion(MCAO).Rempe etal.[3]further saw BBB leakage in the piriform cortex along with impaired tight junctions proteins, pointing that MMP’s interfere with barrier integrity by breaking down these tight junctions proteins[34].Inhibition of MMP’s avoided the tight junctions proteins getting lost [34].Hence although technical problems,present ,initial proof that MMP’s digest tight junctions along with ECMproteins n vivo Is getting demonstrated.
1.7 Studying MMP’s-Various methodologies
MMP’s- have been maximum Evaluated at the mRNA, protein along with activity levels . Utilizing various experimental studies implicating real time quantitative PCR’s along with microarray Evaluation MMP mRNA expression has been documented[35]. MMP protein expression has usually been tested by Western blotting ELISA or by immunohistochemistry .For checking MMP activity in vitro,a commonly utilized method is substrate zymography . Substrate zymography isolates MMP’s by the breakdown of their substrates along with their molecular weight[[36].This technique aids in finding whether MMP is active or latent .Every kind of Substrate zymography started from gelatin zymography,that is utilized to find gelatinases MMP-2 as well as MMP-9[37].For checking the other MMP’s, instead of gelatin collagen,carboxy methylated transferring or casein is utilized [35,38,39].Other technique utilized for MMP activity detection comprise of in vitro are fluorogenic MMP substrates.The artificial substrates are made up of a fluorescent dye which communicates through a peptide to the quencher leading to fluorescence ,that constitutes a direct measurement of the MMP activity[40].
At present it is not feasible to be able to pinpoint the MMP activity in tissues in view of absence of reagents that are appropriate reagents .Only exception is gelatin in situ zymography,a technique which aids in checking MMP-2 as well as MMP-9. gelatin in situ zymography is a manipulation of Substrate zymography in frozen tissue sections of an unfixed sample .In this particular technique an MMP substrates gets shifted to a frozen sections of an unfixed sample.The substrate gets digested by active MMPs in a time along with dose based method,which gets visualized utilizing microscopy[41].More generation of this technique is in vivo zymography[42] in which Substrates get utilized in a live animal for finding the MMP activity in vivo[43].
Methods
Thus a systematic review was carried out using the pubmed and Google Scholar Search engine with the MeSH Terms; Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP’s) along with their inhibitors,namely the, Tissue inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinases(TIMP); MS; cerebral aneurysm,stroke ,epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease(PD) ,Alzheimers disease(AD); brain cancer;Newer MMP inhibitors ;other therapies related to thesefrom 1900 to date in January 2021.
Results
We found a total of 4500 articles out of which we selected 220 articles for this review.No meta-analysis was done .
2. MMPs in diseases of the Central Nervous System(CNS)
2.1 Neuroinflammation
By definition Neuroinflammation represents a nonspecific inflammatory process in the brain .Every Central Nervous System( CNS) disease like multiple sclerosis(MS),cerebral aneurysm,stroke ,epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease(PD) ,Alzheimers disease(AD), along with brain cancer-possess a Neuroinflammatory part which implicates MMPs
The modes by which MMPs result in Neuroinflammation are i) MMPs activate Neuroinflammatory pathways.This gets achieved by indirect activation of enzymes which work on signalling molecules like cytokines , cell surface receptors ,cell-cell adhesion Molecules,or clotting factors[44,45]. Alternate method is MMPs directly activate Neuroinflammatory pathways.Like MT4 – MMP possesses a TNF-α convertase activity via which trans membrane TNF-α gets proteolytically changed into soluble active TNF-α[46].ii) MMPs by themselves work as Neuroinflammatory signalling Molecules.On stimulation utilizing lipopolysaccharides(LPS) , apoptotic signals ,or in PD, neurons liberate active MMPs into the interstitium ,that stimulates microglial activation along with generation as well as liberation of pro inflammatory cytokines(figure4[2][47,48].
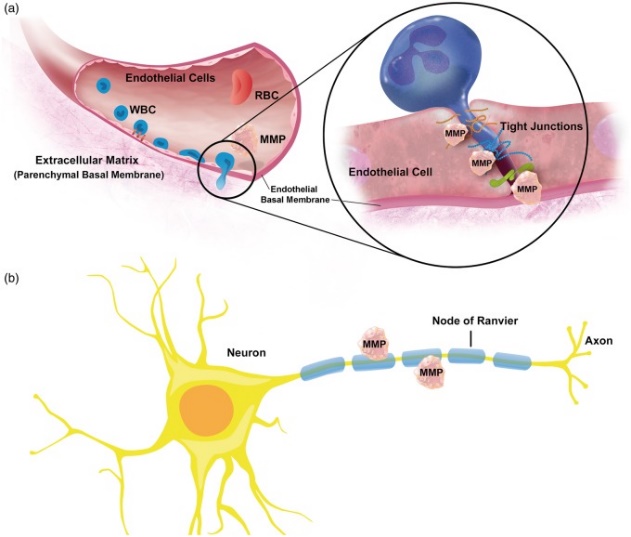
Legend for Figure 4.
Courtesy ref no-3-MMPs in neuroinflammation. MMPs contribute to neuroinflammation through four mechanisms. (1) MMPs activate neuroinflammatory pathways and/or neurosignaling components. (2) MMPs act as signaling molecules themselves. (3) MMPs contribute to neuroinflammation-mediated neurotoxicity. (4) MMPs compromise vascular integrity resulting in blood–brain barrier leakage.
Iii) MMPs aid in Neuroinflammation modulated neurotoxicity via shedding death Molecules like the Fas ligand ,by influencing gamma amino butyric acid(GABA) as well as glycine amounts ,that manipulate chloride channel activity, by stimulation of glutamate receptor - modulated excitotoxicity,or by changing cell-ECM Crosstalk[49,50]. Nevertheless, the precise mode via which MMPs result neurotoxicity are not totally clear in (figure4[3][51-53].iv) Neuroinflammation stimulated MMPs might proteolyze cerebrovascular BM as well as tight junctions proteins,that could reduce vascular integrity causing barrier leakage as well as extravasation (figure4[4][54-56].
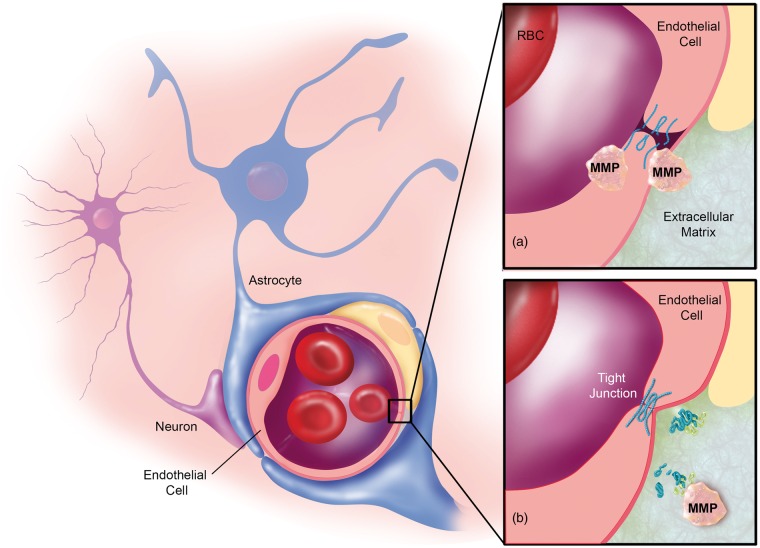
Legend for Figure 5.
Courtesy ref no-3-MMPs in multiple sclerosis. (a) Brain endothelial cells and leukocytes secrete MMPs, which are thought to degrade tight junction and extracellular matrix proteins leading to extravasation of immune cells. (b) Leukocytes, microglia, neurons, and reactive astrocytes secrete MMPs, which demyelinate neuronal axons
Overall, MMPs get stimulated by as well as aid in Neuroinflammation via different modes .Further MMPs aid in inflammation stimulated barrier impairment with facilitation of propagation of different diseases of the CNS(MS,cerebral aneurysm,stroke ,epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease(PD) ,Alzheimers disease(AD),brain cancer).
2.2 Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple Sclerosis(MS), represents a Neuroinflammatory autoimmune disease which influences roughly 1.3 million people worldwide[57,,reviewed by us58].The myelin sheaths which envelope Neuronal axons as well as nerve fibers in the brain along with spinal cord are injured,that interferes with the Crosstalk as well as results in a broad kind of disease symptoms[59].
In MS the part of MMPs have been markedly Evaluated both in animal models along with human tissue[60--62].These studies demonstrated that MMPs digest myelin basic proteins,that results in de myelination along with promotes MS propagation (fig5(a)[56,63]. Utilizing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) animal models of MS various subgroups evaluated MMPs in the brain, brain capillaries , endothelial cells ,spinal cord ,lymph nodes along with spleen demonstrating that a lot of MMPs were enhanced at the time of peak EAE stage [61,64-66]. Particularly in EAE mouse as well as rat model , mRNA as well as proteins amount got escalated for MMP-2,-3,-8,-9,-10,-11,-12,-13,-28 MT1 – MMP, as well as MT6 – MMP.Conversely mRNA as well as proteins for MT2-5 – MMP as well as MT21 – MMP were reduced in lumbar along with sacral spinal cord tissue of EAE mice[67].Whereas the result of reduced MMP’s amount, Specifically, those for MT – MMP’s were not understood ,it is well known that enhanced MMPs accelerate the disease severity in EAE rodent models[60,61,64,65,68].
One property of MS), is leukocytes extravasation along with trans migration via the Brain endothelium into the CNS. MMPs might promote this event via activation of adhesion Molecules along with breakdown of the BM which surrounds blood vessel (figure4[1] as well as [5]. Nevertheless, this is conflicting as no definitive proof is existing.Agarwaletal. demonstrated that selective MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 modulated cleavage of dystroglycans,that is a correlator among astrocytes endfeet along with parenchymal BM Molecules .This event exists at post capillary venules ,where extravasation takes place[60]. Nevertheless, this as well as other studies like study of Buhler etal.[61], pointing that MMPs are implicated in immune cell extravasation into the brain at the time of EAE.
Studies utilizing Brain tissue,serum cerebrospinal fluid(CSF) samples from MS patients,repeatedly observed escalated protein amounts for MMP-2,-3,-7,-9,-12,-13 along with MT1 – MMP[61,69-71].In these studies , leukocytes were isolated as the main liberator of MMPs,the one maximum evaluated in MS is MMP-9, MMP-9 mRNA as well as proteins along with activity amounts are escalated in mononuclear blood cells ,serum as well as CSF along with are linked with barrier impairment along with disease propagation[72-74].
Immune cells from the blood can cross the BBB through a trans cellular(possibly no MMP’s implicated )or a paracellular(MMP’s implicated)pathway .Regards to para cellular pathway,it has got demonstrated that T cells , monocytes, along with dendritic cells express as well as liberate active MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 that open the Brain endothelial tight junctions to pass through the barrier along with shift to the brain[60,75-78]. Following passage via the tight junctions, MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 cleave the transmembrane receptor β- dystroglycans,that fixes astrocytic endfeet to the BM[60]. Additionally, in case of lesional MS tissue,MMP-1,-2-3,-9 along with - 19 got isolated in the microglial nodules as well as microglial like cells where they aid in inflammation as well as derail the BBB more[79,80].
The MMP that gets highlighted in the MS field is MMP-12,that is known as macrophages Metalloproteinase,is presumed to be necessary in the etiopathogenesis of MS,most probably secondary to its primary myelin or oligodendrocyte –toxic potential along with its part in macrophages extravasation[81]. Simultaneously, MMP-12 KO mice with(EAE had a many fold less deteriorated robust severity along with disease burden as compared to EAE wild kind mice , pointing that escalated MMP-12, expression amounts are protective in MS[65].An extra study demonstrated that wild kind along with MMP-12, KO mice with EAE were more robust along with their remaining disability at remission was greater.
Hence although clarification is there that MMP aids in MS,it is less understood if this takes place by breaking down the endothelial BM, that might promote leukocytes getting extravasated along with shifted to the brain(figure5(a]).In the brain leukocytes then liberate greater MMPs which aid in the total MMP action on axonal demyelination besides neuronal cell death.
2.3 Cerebral Aneurysms
Aneurysm by definition is a blood filled –bulge appearing like a balloon in the arterial wall.The etiology of brain aneurysms are multiple. Like aging, atherosclerosis, hypertension ,robust head injury ,all of which are associated with Neuroinflammation[82].Maximum cerebral aneurysms do not get diagnosed till rupture,that remains life-threatening [83].Thus it is key to avoid rupture by utilizing invasive brain surgical intervention[84].Lower invasive technique would be to avoid generation of aneurysms,that needs insight of aneurysm pathology .As per one theory MMPs breakdown the vascular extra cellular Matrix ,thus aiding in limited area of ballooning of a blood vessel resulting in Aneurysm generation as well as growth[85,86].Like human brain samples , protein expression amounts of plasmin, MMP-2, MMP-9, along with MT1 – MMPs were escalated in the wall of the aneurysm as compared to normal Cerebral arteries as well as in total MMP-2/ MMP-9 proteolytic activation was greater in aneurysm tissue as compared to control arteries[85].
Current reports point that MMPs are implicated in vascular calcification [87,88],that could be an extra negative action of MMPs aiding in the pathological result of cerebral aneurysms.The calcification presence as revealed in a retrospective study ,was the only marker of poor result[89].It was observed that larger Aneurysms are more likely to be calcified,whereas size by itself did not cause a poor action on the result.Moreover, in surgically securing intracranial Aneurysms tend to be an important cause of morbidity[89].
A way of minimizing aneurysms propagation as well as growth is via MMPs inhibition ,that could probably decrease the requirement for invasive treatment[90,91].Pre clinical studies illustrate that MMPs inhibitors block the aneurysms generation as well as growth [91-93].Xiong etal.,[93] documented in a mouse model of Marfan syndrome that inhibition of MMP-2, as well as MMP-9, expression of protein utilizing doxycycline blocked ECM breakdown that significantly postponed the aneurysms rupture.Another study utilizing a mouse model, in whom 70% of animals had brain aneurysms generation as by Nuki etal’.,[92], showed that doxycycline decreased the aneurysms incidence by 10%.They further documented a decreased incidence(40%) of intracranial aneurysms in MMP-9 KO mice,while greater than 60% of MMP-2 KO mice, still generated cerebral aneurysms , pointing that MMP-9 is key for aneurysms generation, statins got utilized in rats by Aoki etal.,[94,95],in whom Cerebral Aneurysms, got induced by unilaterally ligating the common carotid artery as well as hypertension .Therapy with statins reduced aneurysm size by 30-40% within one mth possibly via a mode which reduced MMP amounts,that is believed to postpone Aneurysms generation as well as growth[91].The mode by which statins achieve this is related to their cholesterol-reducing, anti inflammatory, along with NFκB actions ,that reduce MMP action[91].Even in humans statins got evaluated.A retrospective study was conducted by Yoshimura etal.,[96],where they Evaluated results from 117 patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms for Evaluating if statins avoid rupture.9% of patients in this study with ruptured cerebral aneurysms utilized statins ,whie 26% of patients with unruptured cerebral aneurysms utilized statins,that pointed that statins reduced the risks of rupture of cerebral aneurysms .
Overall, MMPs aid in generation , growth along with rupture of cerebral aneurysms by ECM breakdown, that results in ballooning of blood vessels.Thus MMPs inhibition , particularly MMP-9 might avoid cerebral aneurysms potentially .
2.4 Stroke
Stroke was responsible for 7 million deaths all over the world in 2012,that is about12%of all deaths ,putting Stroke as the number 2 cause of mortality[97]. Additionally, 10 million people survive following a Stroke/year,with greater than 30 million people in total who got over an earlier stroke[98].The properties of stroke represent lost brain function due to i)reduced Cerebral blood flow (ischaemic) secondary to a blockade of a blood vessel , or ii) secondary to bleeding into the brain parenchyma or subarachnoid space(haemorrhagic).
MMPs result in a harmful action in the acute phase ,while it proves to be advantageous in the post stroke phase[99].The harmful action is brought about by impairment in regulation of MMPs,constituting i) neurovascular interference along with brain parenchymal damage(figure6(a).Different studies Evaluating human as well as rat brains demonstrated that protein along with activity amounts of MMP-2,-3 as well as -9 are escalated following a stroke as well as MCAO as compared to control tissue[100,101].Such alterations in MMP-2,-3 as well as -9 protein along with activity amounts cause abnormal proteolysis which aid in Blood Brain Barrier impairment,that partly decides the degree of the infarct[100-102]. Additionally, studies utilizing rat stroke model points that by breaking down the basal lamina, MMPs escalate the proneness of Brain capillaries to rupture along with haemorrhagic conversions following a stroke[103,104].Other harmful actions of MMPs in stroke got demonstrated in studies utilizing rodent models of focal Cerebral ischaemia.In these studies, escalated MMP-9 protein amounts were observed in the acute phase(12-24h) following stroke which concurred with the opening of the Blood Brain Barrier. As compared to that MMP-2 protein amounts were escalated lot of days following stroke[105],at the time when barrier leakage probably gets reinstalled.
Whereas maximum work on MMPs in stroke has concentrated on MMP-2 as well as MMP-9[106],other MMPs also possess harmful actions. Following treating mice subsequent to thrombotic MCAO utilizing tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA),Suzuki etal.,[107] demonstrated an escalated incidence of intracranial bleeding as compared to mice not receiving tPA therapy.They demonstrated an escalated MMP-3 mRNA along with protein amount in the capillary endothelium in the infarct area of tPA treated mice as compared to tPA untreated control mice. Thus conclusions of Suzuki etal.,[107,108] werethat in case of tPA receiving mice MMP-3 digested the neurovascular basal lamina,thus opening of the endothelial Barrier as well as aiding in the intracranial bleeding. Such observations pointing that MMP-3 has harmful actions at the time of tPA therapy or gets stimulated by tPA ,unfortunately as at present tPA is the only therapy that received FDA approval for the ischaemic stroke.
Nevertheless, MMPs further had advantageous actions at the time of recovery phase following stroke(figure6[b])[109].Studies pointed that MMP-9, MMP-2, as well as MMP-7 , refashion the lesional ischaemia along with infarcted tissue In addition to take part in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis, along with neurogenesis[110,111].Two modes got isolated by which MMPs carry out these actions i)at the time of tissue refashioning in the post –stroke recovery along with healing phase MMPs digest old ECM,in view of new ECM as well as tissue could get developed[3,109,112].ii) at the time of ECM digestion, MMPs(major MMP-7 along with MMP-9 but MMP-1,-2-3-10 as well as 11) escalate the growth factors that could be attained(like nerve growth factors , Brain-Derived neurotrophic factor( BDNF), neurotrophin3/4, along with vascular endothelial growth factors( VEGF).This takes place via cleavage of the inactive growth factor precursor into their active form or via liberation of active growth factor by proteolysis of ECM [110]. Escalated amounts of growth factors aid in tissue remodeling by stimulation, of angiogenesis, vasculogenesis, along with neurogenesis,all of them that are key in stroke recovery.These observations pointing that at the time of remodeling as well as healing event , MMPs are implicated in the migration of neuronal precursor cells to the areas injured by stroke[113].
Overall , MMPs are necessary in stroke in the acute phase as well as post –stroke recovery phase(figure6).In the acute phase, MMPs interfere with the Barrier integrity In addition to injure the parenchymal tissue,while in the post –stroke phase by refashioning lesional ischaemic as well as infarcted tissue along with take part in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis, along with neurogenesis.
2.5 Epilepsy
As per the World Health Organization(WHO),a minimum of 65 million people in the world are afflicted by Epilepsy[114,115]. Epilepsy encompasses different diseases along with seizure syndromes , In addition to get diagnosed with epilepsy following recurrent ,unprovoked seizures[116].
The part of MMPs in Epilepsy remains uncertain at present , nevertheless, studies point that MMPs aid in epilepgogenesis, epilepsy propagation along with brain remodeling following seizure.Like MMP-9 KO mice possess lowersensitivity to chemically-stimulated seizures as compared to wild type mice, whereas on the other hand human MMP-9 overexpressing rats possess greater sensitivity to chemically-stimulated seizures pointing that MMP-9 influences epilepgogenesis as well as /or seizures generation[117,118].
MMP amounts are escalated in the epileptic brain. In case of chemically-stimulated seizures models along with temporal lobe epilepsy, MMP-9 protein as well as activity amounts are escalated in neurons of the parietal along with frontal cortex, in addition to the thalamus, the areas where the seizures got initiated [51,118-120].Li etal.[121], observed escalated MMP-9 protein as well as activity amounts in CSF in adult epilepsy patients with generalized tonic –clonic convulsions as compared to age matched controls or non epileptic persons. MMP-9 protein amounts were further observed to be escalated in serum from patients following convulsions. Three times greater MMP-9 protein amounts were further observed by Suenaga etal[122],in serum from children with encephalopathy subsequent to post febrile seizures, along with children with convulsive status epilepticus, in contrast to healthy children[122].As per experimental work escalated MMP-9 protein as well as activity amounts mainly possesses 2 functions i) MMP-9 aids in seizures stimulated neuronal cell death as well as ii) MMP-9 is key in refashioning neuronal networks following seizures. Neuronal cell death in regions, possessing escalated MMP-9 amounts was illustrated by Jourquin etal.[52], as well as Hoehna etal.[51], along with documented that inhibitors of MMP-9 decreased cell death .Other studies revealed that MMP-9 is implicated in structural remodeling, mossy fiber sprouting ,reduced seizures stimulated trimming of dendritic spines along with reduce abnormal synapses generation[118,120,123].
The part of MMP-2 in the epileptic brain is poorly known as compared to MMP-9. Jourquin etal. .[75], demonstrated that MMP-2 does not aid in neuronal cell death in epilepsy. Nevertheless, it is feasible that MMP-2 aids in structural remodeling in epileptogenesis as MMP-2 mRNA, protein as well as activity amounts are escalated following convulsions[118,120,124]
Various sources revealed that Blood Brain Barrier impairment exists in epilepsy along with seizures stimulated barrier leakage[125-128].Moreover, this barrier leakage by itself acts as a trigger for seizures, pointing that there is a vicious feedback loop aiding in propagation of epilepsy[128,129]. Possibly MMPs participate by breaking down of tight junctions as well as ECM proteins, that potentially aid in barrier leakage following convulsions[30-32].Li etal.[121], demonstrated that escalated MMP-9 protein as well as activity amounts in serum CSF of patients with generalized tonic –clonic convulsions were linked to barrier leakage. Moreover, this barrier leakage was correlated with leukocytes extravasation into the brain following convulsions. leukocytes extravasation implicates a complicated ,several steps event needing MMPs Specifically, MMP-2 as well as MMP-9,both coming from the endothelium along with activated T cells as well as macrophages[,78,110]. Li etal.[121], demonstrated that in patients with generalized tonic –clonic convulsions that escalated CSF leukocytes counts were associated with enhanced MMP-9 amounts, in CSF In addition to the extent of barrier leakage[201].Hence MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 appeared to aid in seizure as well as /or epilepgogenesis, neuronal networks, remodeling, neuronal cell death as well as barrier leakage following seizure.About the rest of MMPs not much insight exists in epilepsy.
2.6 Alzheimers disease (AD)
Alzheimers disease(AD ) represents a Neurodegenerative disease which implicates greater than 20million patients worldwide[130,131].Further it has been anticipated that about 100 million patients of AD would be there by 2050[132].Inspite of all research work ,the etiopathogenesis along with propagation remains ill understood ,besides the treatment or avoidance is not present right now.The pathology of AD has the properties of brain collection of amyloid beta(Aβ), generation of amyloid beta plaques, generation of neurofibrillary tangles along with Neuroinflammation,all of whom aid in Neurodegeneration [133,reviewed by us 134-139].
Various groups demonstrated that MMP amounts in rodent models of AD are enhanced as compared to control animals. Enhanced MMP-9 protein amounts were observed in brain slices from transgenic amyloid precursor protein (APP)/PS1 mice , in contrast to wild kind mice was revealed by Yan etal.[140]. Utilizing 5x FAD mice ,Py etal.,[141]found escalated MMP-2, MMP-9,MT1- MMP amounts in the hippocampus in contrast to control mice.Primarily MMP-2, as well as MMP-9, were expressed in astrocytes,while MT1- MMP were seen in neurons, MT1- MMP as well as MMP-9, were also observed in amyloid beta plaques.Validating these observations various groups found overexpression of proteolytic activity MMP-2,-3 -9mRNA as well as protein in post-mortem brains from patients of AD[142,143] . Utilizing zymography , Horstmann etal[144], found MMP-2,-3 -9, as well as -10 activity amounts in serum along with CSF from patients of AD as well as contrasted them to gender along with age matched healthy control persons from patients of AD.They detected that MMP-3 activity was escalated by 40% in plasma along with 60% in CSF patients of AD as compared to control persons was reduced by 32% in contrast to CSF samples from healthy control persons ,whereas activity amounts were unaltered in plasma ,along with MMP-9 as well as MMP-10 activity were not found in CSF, MMP-9 activity in plasma was reduced by 41% as compared to healthy control persons . Greater amounts of pro- MMP-9 protein in plasma samples from AD patients as compared to control persons.Lorenzi etal.,[145]observed greater amounts of pro MMP-2 protein in plasma samples from patients of AD in contrast to control persons .
Certain work was conducted for getting insight into the correlation of MMPs along with Aβ.Deb as well as Gottschalk [146] revealed that in rat hippocampal along with astrocytes cultures that Aβ40 stimulated protein expression in addition to proteolytic activity of MMP-2,-3 -9.They documented that by exposure of segregated rat capillaries to Aβ40 ex vivo enhanced MMP-2, as well as MMP -9 protein along with activity amounts[147].Findings akin to these were made in a transgenic mouse AD model(Tg 2567 hAPPmice),where MMP-2, as well as MMP -9 amounts in brain capillaries were escalated in contrast to capillaries wild kind mice.Yin etal.[148], found in APP/PS1 mice that astrocytes that surrounded amyloid beta plaques liberated greater MMP-2, as well as MMP -9 amounts.They further illustrated that on breeding APP/PS1 mice with MMP-2 or MMP -9 KO mice,or pharmacologically inhibited MMP-2 or MMP -9 in APPsw mice amount,enhanced Aβ brain amounts by 1.5fold, in contrast to controls along with enhanced Aβ half life by approximately 50%[229].Further Yin etal.[149], revealed in the phosphate buffer –insoluble fraction of cortex as well as hippocampus of MMP-2 KO mice escalated murine Aβ40 along with Aβ42 in contrast to age matched wild kind mice,while Aβ40 along with Aβ42 continued to be unaltered in the phosphate buffer –insoluble fraction .In the cortex of MMP-9 KO mice,murine Aβ42 amounts were escalated inthe phosphate buffer –soluble fraction of cortex as well as hippocampus in contrast to age matched wild kind mice,whereas they continued to be unaltered in the phosphate buffer –insoluble fraction.These actions were secondary to reduced Aβ proteolysis as well as were not related to escalated Aβ generation.These observations pointed that MMPs potentially aid in Aβ clearance .Concerning this MMP-2,-3 as well as MMP -9 proteolytically break down Aβ[140,149,150].It was revealed by Ridnour etal.[151],that amounts of Aβ1-16, that is a product of Aβ metabolism by MMP -9 along with MMP -9 activity were reduced in brain lysates of hAPPSwD1 mice where nitric oxide synthase(NOS) was absent in contrast to their littermates that expressed NOS .On the basis of these outcomes ,they concluded that potentially nitric oxide (NO) is implicated in clearing the plaques, via escalated MMP -9 activity.Yan etal[140], documented that in brain slices of APP/PS1 mice in situ that MMP -9 digests the fibrillary Aβ42 along with compact amyloid plaques.The in vivo association among MMP -9 protein expression along with Aβ plaques, was Evaluated by Wang etal.,[152] by deletion of the MMP -9 gene in APP/PS1 mice. Aβ plaques, were greater in size along with number ,in the cortex as well as hippocampus of these APP/PS1 MMP-9 KO mice, in contrast to APP/PS1 mice possessing functional MMP -9.Lastly Liao etal.[153] illustrated that MT1- MMP breaks down both soluble in addition to fibrillary Aβ peptides in a time –based way in vitro along with this action gets inhibited by MMP inhibitors GM 6001 along with TIMP2. Liaoetal.[153], further demonstrated that MT1- MMP breaks down brain fibrillary amyloid plaques in another mouse AD model(hAPPSwD1) in situ .
These observations point to an inverse association with MMP-2/ MMP-9 along with Aβ,where one anticipates lower MMP-9 amounts in the AD brain possessing larger Aβ loads. Nevertheless, MMP’s are upregulated in the AD brain ,that is separate from what one predicts with the findings observed earlier.1 reason for this might be that MMP-modulated Aβ breaking down is markedly less to avoid Aβ collection in the brain.Whereas MMP’s might be implicated in the Aβ processing along with clearing off the plaques they do not seem to be potentially the main actors in this event [140,148].
Hence MMP’s are escalated in the AD brain, Nevertheless, the part played by them in AD remains unclear.The present literature available is not sure on if MMP’s aid in AD propagation or may possess an advantageous role on this disease. Whereas probability exists that MMP’s have no main role in AD,studies illustrated that MMP’s could probably be implicated in processing Aβ along with AD propagation.
2.7 Parkinson’s disease (PD)
Parkinson’s disease(PD) represents a Neurodegenerative disease implicating movement aberration where over 6 million patients are afflicted world over[154].In 1817 it was initially detailed by James Parkinson[155],although many details of the disease remain unclear. Molecularly, PD has the properties of collection of α-synuclein in the dopaminergic neuron leading to the generation of Lewy bodies ,cell injury along with neuronal death of dopaminergic neurons .Further PD is associated with Neuroinflammation that accelerates the disease[156].
In the field involving PD, MMP’s have got evaluated. MMP- 1,2 as well as 9 protein as well as activity amounts were evaluated by Lorenzi etal.,[157] in postmortem brain tissue from PD patients with age –matched control persons . Whereas they did not find any alteration in MMP-1 as well as 9,they observed a decrease in 50% in MMP-2 activity amounts in the substantia nigra [151].
Besides MMP-1,2 as well as 9,work on PD has concentrated basically on MMP-3.Three modes have been offered regarding how MMP-3 might be implicated in PD .i) Utilizing in vitro cell lines along with primary cultures of dopaminergic neurons from rat Choi etal.,[158] saw that active MMP-3 gets liberated from apoptotic dopaminergic neurons In addition to,that MMP-3 protein amounts were greater in contrast to healthy non apoptotic dopaminergic neurons. Utilizing the MPTP mouse PD model ,Chung etal.,[156] observed escalated MMP-3 protein as well as activity amounts in contrast to control mice leading to apoptosis as well as cell death. MMP-3 is further implicated in caspase-3 activation, particularly in apoptotic signalling upstream of cJun N-terminal kinases [156,158].ii) MMP-3 might have potential role in α-synuclein cleavage .Sung etal.,[159] illustrated that MMP-3 cleaves purified α-synuclein in vitro along with that α-synuclein accumulation escalatedin the existence of MMP-3 cleaved α-synuclein fragments in contrast to a solution not possessing these fragments.Moreover ,collected α-synuclein fragments possessed higher toxicity in cell viability assays in contrast to collections of nonfragmented α-synuclein.Further Sung etal.,[159] documented that MMP-1,2 as well as 9 along with MT1- MMP cleaves purified α-synuclein also, Nevertheless,they possessed lesser efficacy as compared to MMP-3.Further more Kim etal .,[160] demonstrated in microglial cultures along with 6OHDA mouse PD model that α-synuclein -stimulated cell migration of reactive microglia into the pathological area ,that augmented PD pathogenesis.iii)Current work points that neuroinflammatory process is implicated like microglial activation,T leukocytes infiltration along with Blood Brain Barrier impairment in PD[156,161].This validates ,Chung etal.,[156] results who demonstrated that infiltration of peripheral immune cells along with brain uptake of FITC –albumin (70kDa)in the MPTP mouse PD model, pointing thatneuroinflammation along with barrier leakage .They revealed in MMP-3 KO mice that barrier leakage got ameliorated Besides the reduction of immune cells numbers infiltrating the substantia nigra got reduced , illustrating MMP-3 implication in the MPTP mouse PD model.
Thus concluding ,that MMP-3 appears to be implicated in dopaminergic Neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation along with barrier leakage.More work is required for clarification of the part of MMPs in PD along with whether MMP inhibition might turn out to be a fruitful treatment method.
2.8 Brain Cancer
Over 250,000 people got diagnosed with a newly diagnosed Brain Cancer with about 190,000 patients dying world over with the same in 2012[162]. Brain Cancer patients possess a very poor survival rates.Despite aggressive treatment, the median survival of patients with glioblastoma multiforme ,that is amongst the commonest along with a very aggressive malignant Brain Cancer, is only 12-17 mths [163,164].Thus for efficacious therapy of Brain Cancer, newer novel strategies along with interventions arerequired. MMPs serve as those potential targets in cancer in view of their part in Cancer biology .Thus , mRNA along with protein overexpression of MMP-1,-2,-3,-7,-8, 9,-13, as well as MT1- MMP has been illustrated in a lot of malignant peripheral along with CNS tumors ,besides an association among MMP expression, tumor acceleration rate, staging of tumor along with prognosis has been revealed[165].Actually liberated MMPs( MMP-1,-2,-3,-7,-8, 9, as well as -13) along with membrane bound MT- MMPs are key for the generation of Cancer metastases,their invasion into the brain along with the generation of secondary tumors,with MMPs taking part in maximum steps of this metastatic event(figure7)[166,168].
i) Generation of metastatic cells at the initial tumor-In case of primary tumor,Li et al.,[165] demonstrated that MMP-7,transforms the transmembrane cell-cell adhesion protein E-cadherin into a soluble protein leading to inefficacious binding among tumor cells ,that lets the Cancer cells to detach from the primary tumor along with Generate metastases having the capacity of entering the blood stream .
ii) metastatic cells intravasating into the blood circulation-Junker Jenson [168],observed that MMP-1,- takes part in the metastatic cells intravasating from a human Hep3 epidermoid carcinoma graft to chick embryos .They demonstrated that MMP-1 controls endothelial permeability along with trans endothelial migration validated tumor invasion via activation of the endothelial non tumor/non matrix receptor PAR1. Junker Jenson [168], further utilized grafts with naturally acquired or experimentally stimulated MMP-1 reduction ,observing that intravasation got reduced by greater than 80%[168].
iii) adhesion of metastatic cells with the brain capillary endothelium –it is not clear if MMPs take part in this particular step of the metastatic event , nevertheless,knowing the different functions MMPs possess this is feasible.It was illustrated by Hummel etal.,[169]that MMP-2,-3, 9, as well as -12 are implicated in the shedding of cell adhesion Molecules (like vascular cell adhesion molecule[VCAM-1])from the plasma membrane of human brain endothelium cells following TNF-α stimulated MMP upregulation. MMPs might further aid in shedding CD44 in metastatic cells adhesion with the brain capillary endothelium[170].This is Specifically significant in view of CD44 being a cell surface glycoprotein in endothelial cells, leukocytes along with a lot of metastatic Cancer cells,where it delivers selectins thus promoting adhesion of the host cell to the brain capillary endothelium[171].
iv) extravasation of metastatic Cancer cells- MMPs aid in extravasation of metastatic Cancer cells along with promote paracellular trans migration of tumor cells across brain capillary endothelial cells in vivo,besides the Blood Brain Barrier in vitro[172,173].That MMP-2 aids the migration of the breast Cancer cells across the cell m layer of an in vitro human Blood Brain Barrier model was demonstrated by Lee etal.[172]. Felding –HabermannB[173] revealed in vivo how breast Cancer cells injected into the left carotid artery of BALB/cmice lead to brain metastases.Regards to paracellular extravasation, endothelial cell – cell contacts have to be loosened so that metastatic cells can move across the endothelium.For this junction proteins are needed to be breaking down.Actually MMPs proteolyse tight junctions as well as adherence junctional proteins, thus opening the paracellular route[,30,31,165].Feng etal.,[30] ,illustrated in leukaemic BALB/c nu/nu mice that leukaemic cells liberate MMP-2 as well as MMP-9,that broke down the tight junctions proteins zona occludens -1,claudin-5 and occludin.Hence MMPs are key for leukaemic as well as other cells to cross the capillary endothelium as well as get entry into brain .
v) metastatic cells adhesion to the ECM-various membrane type MMPs(MT1-,-2,-3,-5) MMPshed the cell being a cell surface glycoprotein CD44,that is key in metastatic cells adhesion to the luminal endothelial membrane along with the ECM on the basolateral side of the endothelium[170,174]. CD44, is implicated in presenting cytokine, chemokine, cells adhesion molecules, growth factors along with other proteins likeMMP2 awa MMP9 to receptors on metastatic along with endothelial cells awa modulates signalling which controls metastatic cell migration along with invasion [174,175]. CD44, further crosstalks with ECM proteins like fibronectin,,thus corroborating metastatic cells adhesion to the ECM[176].
vi)Role of MMPs in ECM proteolysis-localized opening of the ECM(figure7)is essential for metastatic cells to bypass it,with MMP-2 as well as MMP-9,appearing to assist this event via ECM proteolysis. in contrast to control samples Wang etal.,[271] checked the MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 amounts in human glioma samples as well as MMP-2 along with MMP-9 , documented that MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 amounts were escalated in human glioma,besides being associated with the degree of glioma malignancy . Wang etal.,[177] further illustrated that MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 staining in gliomas was limited to the cytoplasm of tumor cells , endothelial cells along with their ECM,Thus concluding that by breaking down the ECM, MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 are the factors that decide how much invasiveness along with angiogenesis gliomas possess[177]. Other studies in Cancer cells documented that CD44, captures MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 at the tumor cell surface, where MMPs then digest locally the ECM that surrounds the tumor cell at the time of extravasation[178].
Other MMPs might further aid in ECM proteolysis.Despite conclusive in vivo evidence to validate this is lacking ,many observations suggest these findings. Escalated MT1- MMP mRNA along with protein amounts in resected Glioblastoma tissue was documented by Shimada etal.,[180] as compared to non- tumor control tissue. MT1- MMP amounts were associated with pro- MMP-2 activation along with tumor malignancy with Shiomi etal.,[180] offering a posit that MMP-2 as well as MT1- MMP probably aid in glioma invasion via breaking down brain ECM proteoglycans besides glia limitans . Escalated MT1- MMP along with MT2- MMP mRNA along with protein amounts were documented by Nakada etal.,[179] in astrocytomas in contrast to control brain tissue. Thus they concluded that both activate MMP-2,which then breaks down the ECM.Other groups revealed that MT3- MMP directly cleaves ECM parts like type III collagen, proteoglycans as well as interstitial collagens[180].These observations are crucial for Cancer metastases as well as as well as invasion as they lead to digestion of ECM.
vii) utilizing metastatic cells migration-for the generation of a secondarytumor, Cancer cells need space on settling in new tissues.This space is probably developed by MMP-modulated ECM breaking down along with remodeling.In this regard Belien etal.,[181] illustrated MT1- MMP digests axonal myelination proteins which inhibits migration of cells along with neurite outgrowth.With the knowledge that invasive glioma cells migrate with preference move along the white matter tracts in addition to MT1- MMP breaks down the cell membrane inhibiting proteins which are enmeshed within white matter fiber tracts ,with these findings pointing that MT1- MMP promotes cell migration ,hence escalatation of glioma malignancy.
viii) MMPs along with tumor microenvironment as well as tumor angiogenesis- escalatation of proof point that MMPs develop along with sustain a microenvironment that promotes tumor growth as well as survival . MMPs promotes Cancer cells proliferation by control of cytokines , growth factors as well as cell adhesion Molecules which attract tumor cells along with aid in the tumor spreading[167].Thus escalatation of MMPs amounts are believed to associate with enhanced malignancy,besides studies document that MMP mRNA, protein as well as activity amounts are escalated in cancer[167]. Escalated MMP-1 as well as , protein amounts in glioma in contrast to amounts in the resected brain tissue in patients with epilepsy were observed by Xu et al.[182]. Amounts of MMP-1,-2,-3,-7,-8, 9, as well as -13, MT1-,-2,-3,-5, as well as -6 MMP were also enhanced in brain tumors in contrast to non cancerous brain tissue[177,178].Same MT MMPs activate pro MMP-2 as well as pro MMP-13,besides protein as well as activity amounts of those MT MMPs are associate with pro MMP-2 activation in gliomas ,thus with tumor malignancy[183,185].MMPs further aid in angiogenesis,that is key for the tumor microenvironment in view of blood vessels feeding the tumors with oxygen as well as nutrients ,thus aiding in tumor survival, growth as well as escalatation of tumor malignancy[179,184]. Angiogenesis depends on endothelial cell migration into the surrounding connective tissues as well as MMPs are key in this event [186]. MMPs break down the ECM, liberation of ECM concealed pro- angiogenic substances like VEGF,process growth factors ,integrins as well as adhesion molecules thus maintaining a balance among pro as well as anti angiogenesis[179,184]. Tumor stimulated angiogenesis is significant in maintaining growth of solid tumors along with the functional part of MMPs in tumor angiogenesis has been well proven [187,188].Like MMPs aid in recruitment of pericytes ,that are present in tumor blood vessels as well as is key for the generation of a functional vascular network . MMPs take part in various steps of recruitment of pericytes. 1stly MMPs break down the ECM for aiding in pericytes invasion.Secondly , MMPs induce pericytes proliferation as well as protection of pericytes from apoptosis.3rd , MMPs aid in recruitment of bone marrow obtained stem cells ,that differentiateinto pericytes[189].
Angiogenesis ,is necessary for tumor growth, hence blockade of angiogenesis is believed to be a good approach for regulation of malignant tumors. Hence MMPs can prove to be advantageous in cancer in view of their anti angiogenic action which is dependent on an processing growth factors ,integrins as well as adhesion molecules.Like tumor angiogenesis is decreased in integrin α1 null mice in contrast to wild kind mice[87]. integrin α1 null mice overexpress MMP-9 that cleaves angiostatin from plasminogen , as well as angiostatin inhibits endothelial cells growth, leading to tumor growth inhibition[190].
MMPs further are implicated in tumor microenvironment by enhancing the permeability of the vascular endothelium in brain tumors, which is then labelled as ‘’blood tumor barrier ‘’.Hence ’blood tumor barrier is leaky in contrast to healthy, intact ’blood brain barrier that aids in feeding the tumor with an enhanced needs of the nutrients[191].It was, illustrated by Noell etal.,[192] that enhanced MMP2.-3 as well as -9immunoreactivity in brain slices of human papillary glioblastomas in contrast to non tumor brain tissue as well as presumed ’blood brain barrier leakage in this region.Studies from different groups revealed pro MMP-2 as well as pro MMP-9 amounts in the CSF of dogs possessing intracranial tumors in contrast to healthy dogs [193,194]. Escalated CSF pro MMPs were described as secondary to the recruitment of leukocytes by the tumor was posited by Turba et al.,[194] that MMPs probably promoted leukocytes bypassing the BBB to be able to reach the tumor, as well as those leukocytes liberated - MMP 9 into the CSF.
Thus , MMP’s are key in many ways in brain cancer .Their major part is in promotion of metastases along with angiogenesis that makes them significant targets for brain cancer therapy along with avoidance of brain tumors.
3. Inhibition of MMP’s for Treatment of brain tumors
MMP inhibitors like batimastat, Marimastat along with doxycycline could be utilized potentially [reviewed by us in gynae mmp 195].At present , Nevertheless,only MMP inhibitors that got approval from FDA is the tetracycline analogue doxycycline(Periostat) for treating periodontal disease[196-197].The biggest hurdle in generation of MMP inhibitors as per clinical utilization in patients is the absence of insight in the complicated MMP biology,besides the part played by them in CNS disorders like multiple sclerosis(MS),cerebral aneurysm,stroke ,epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease(PD) ,Alzheimers disease(AD).However , lot of preclinical results which validate MMP inhibition in the form of therapeutic approach in MS, stroke along with brain cancer.
1st ,a lot of MMP inhibitors reduce the incidence as well as severity of EAE in animal MS models [145,198,199]. MMP inhibitor-Ro-31-9730 repressed EAE in rats[199], as well as minocycline decreased MMP 9 protein along with activity in Tcells ,besides repressing EAE in mice[198].2nd, pre clinical results from mouse as well as rat cancer models that included colon as well as breast cancer demonstrated that batimastat decreased tumor growth, number along with secondary lung as well as lymphatic metastases taking place [200,201].3rd, MMP inhibition utilizing GM 6001 or BB94 in rodent stroke models immediately(hours) following stroke decreased edema, size of the infarct, as well as amount of haemorrhagic processes [107,202]. MMP Inhibition that was of longterm(days) utilizing BB1101 for uptill 48hrs following stroke in rats decreased barrier leakage , nevertheless, their was no improvement in neurologic function as well as in behavioural tests[203]. Inhibition of MMPs utilizing FN-439 or BB94 in a rat stroke models for a week even accelerated ischemic brain damage besides appeared to stop functional improvement[112].
Despite MMP inhibition appears advantageous in animal models ,it has not been, illustrated or only partially ,illustrated in clinical studies.In MS , 16 cases with relapsing –remitting MS got treated with doxycycline/interferon combination for 4 mths(NCT 00246324[204]).This doxycycline/interferon combination decreased brain lesions which was associated with decreased serum MMP 9 amounts as well as improved post therapy EDDS values with just one patient relapsing. In total doxycycline/interferon therapy was believed to be safe, efficacious ,well tolerated,with the conclusion that a trial with greater patient cohort needs to be carried out. Nevertheless, a documentation on a follow up trial has not been published .
In a trial on stroke, minocycline was administered with/without tPA therapy to 60 patients within 6h following stroke(NCT 00630396[205]).The mean baseline NIH Stroke Scale Score was 8.5±5.8(moderate stroke). Minocycline did not result in severe haemorrhages in patients receiving tPA therapy,was believed to be safe as well as well tolerated,upto 10mg/kg,iv alone or in with combination with tPA ,thus believed to be ideal for a combination tPA therapy.Lampi et al.,[206], in another clinical study ,illustrated that minocycline improved patient results significantly . Particularly, NIH Stroke Scale, as well as Rankin Scale Scores were lowered significantly along with the Barthel Index was significantly escalated .Further more participants are still under recruitment for a study Evaluating the safety as well as effectiveness of Minocycline in acute cerebral haemorrhage(MACH Trial NCT 01805895).
Finally ,various clinical studies Evaluating the MMP inhibition in brain cancer have been carried out.In 2 phase II trials, a combination of Marimastat as well as temozolomide was evaluated for recurrent GBM along with gliomas[[207,208]. These trials revealed that Marimastat as well as temozolomide seems to enhance propagation –free survival (PFS):at 6mths , PFS. 39% for GBM(target PFS40%) as compared to temozolomide alone.Other brain cancer trials with MMP inhibitors demonstrated no improvement .Prinomastat as well as temozolomide as compared to temozolomide alone did not improve 1 yr survival or PFS (NCT 00042004147[209]Pfizer ).Akin to that phase I as well as II trial with the MMP inhibitor COL-3 in recurrent high grade gliomas do not demand more studies(NCT 00042004147[308,9]). Additionally, clinical trials Evaluating greater than 50 MMP inhibitors for cancer therapy have failed [210-214].Vandenbrouke and Libert[213] summarizing the causes for failure ,included complicated MMP biology , as well as absence of insight into MMPs .Further suboptimal trial design ,inadequate clinical endpoints ,utilization of metabolically unstable MMP inhibitors ,poor oral bioavailability ,no action ,toxic side effects as well as discrepancies in preclinical animal model as well as human patients[213].Thus whereas lot of work has been done in MMP research over decades ,this field is distant from a treatment breakthrough .Hence greater work needs to be conducted to Evaluate if MMP inhibition can be a viable approach for treatment.
4. Conclusions
Thus we have summarized the insight in the part played by MMPs in health along with disease , Specifically, the BBB.Whereas we have knowledge that take part in significant neuro physiological functions alomg with have basic insight of their part like Neuroinflammation,MS,Stroke ,awa brain cancer ,little is clear regards to MMPs in other conditions like cerebral aneurysm,stroke ,epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease(PD) .
Lot of varied MMPs possess a wide range of separate function in different physiological as well as pathological events leading to both advantageous along with harmful actions within the same disease based on their presence ,time point, as well as other factors.Hence MMP expression along with functional action differ importantly ,besides being context –base. Nevertheless there is one common denominator in all diseases that is Neuroinflammation which implicates MMPs.
From what we have learnt is MMP inhibition is an extra treatment choice remains a problematic issue with history of failure ,but still detailed in therapy of CNS conditions.Other than doxycycline nothing has therapeutic significance .Knowing the gap in our understanding greater insight needed for preventing the earlier mistakes . Particularly ,research just concentrated on MMP-2 as well as MMP-9 requires to be broadened to include rest of MMPs to get insight in their part in health as well as disease regards to MMP biology generally.Like finding the mode of action controlling the MMP s could give newer therapeutic options .Further Particular as well as selective MMP inhibitors which can get safely utilized with nil or just minor side actions need to be isolated.
Our insight in getting MMP biology regards to health as well as disease is just seeping in .Future MMP inhibitors like the one quoted earlier might aid in epilepsy therapy ,developing ECV related to NDEV in therapy of AD as well as utilization of natural products like from honey etc are getting explored besides for brain cancer newer methods getting designed.
Further Broekaart et al. observed in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsyalong with status epilepticus patients . Using quantitative PCR (qPCR) and immunohistochemistry, they studied the expression of MMPs and their endogenous inhibitors tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) in patients with status epilepticus (SE) or temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) and in a rat TLE model. Furthermore, we tested the MMP2/9 inhibitor IPR-179 in the rapid-kindling rat model and in the intrahippocampal kainic acid mouse model. In both human and experimental epilepsy, MMP and TIMP expression were persistently dysregulated in the hippocampus compared with in controls. IPR-179 treatment reduced seizure severity in the rapid-kindling model and reduced the number of spontaneous seizures in the kainic acid model (during and up to 7 weeks after delivery) without side effects while improving cognitive behavior. Moreover, our data suggest that IPR-179 prevented an MMP2/9-dependent switch-off normally restraining network excitability during the activity period. Since increased MMP expression is a prominent hallmark of the human epileptogenic brain and the MMP inhibitor IPR-179 exhibits antiseizure and antiepileptogenic effects in rodent epilepsy models and attenuates seizure-induced cognitive decline, it deserves further investigation in clinical trials[215]. Gu et al[216] studied thirty‐one patients with AD and 15 cognitively normal controls (NCs)for evaluation of plasma neuronally derived extracellular vesicle (NDEV) levels of core pathological markers [amyloid‐β (Aβ) and phosphorylated tau] and inflammatory biomarkers, including interleukin 6 (IL‐6) and matrix metalloproteinase‐9 (MMP‐9) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
The diagnosis of AD was supported by fluorodeoxyglucose and Pittsburgh Compound‐B PET scans. Plasma extracellular vesicles were extracted, precipitated, and enriched for neuronal source by anti‐L1CAM antibody absorption. Levels of Aβ42, P‐T181‐tau, P‐S396‐tau, IL‐6, and MMP‐9 in plasma NDEVs were quantified by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
They observed Aβ42, P‐T181‐tau, and MMP‐9 levels in plasma NDEVs were significantly greater er in patients with AD than NCs. However, P‐S396‐tau and IL‐6 levels in plasma NDEVs did not vary among AD patients and NCs. Moreover, there was no association among any of these biomarker amounts and cognitive function as measured with Mini‐Mental State Examination in patients with AD.Thus concluding that levels of core pathological markers, including Aβ42 and P‐T181‐tau, are escalated in plasma NDEVs of patients with AD. Furthermore, MMP‐9 might play a significant part in the pathogenesis of AD, and is a promising inflammatory biomarker for AD.[216]
Propolis is a common product of the beehive,which has a large number of therapeutic properties. Royal jelly (RJ) is a bee product that is fed to bee queens during their whole life, and it aids in their great physical fitness, fertility, and long lifespan. Evidence points that propolis and RJ can facilitate health by avoiding the occurrence of age-related debilitating diseases. Therefore, they have been used to treat different robust conditions like diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. Some evolving studies used these bee products to treat PD in animal models. However, a clear insight of the collective effect of propolis and RJ as well as their mechanistic action in PD is absent . Thus Mohammad Ali and Kunugi evaluated the available literature for the actions of propolis and RJ on PD. They tried to explain how MMPs might be influenced through these bee products.[217].
Earlier Li etal.had Evaluated the differential expression of same miR-338-5p of the sa miR-338-5p in gliomas and the role of miR-338-5p in glioma cell invasion via its potential target gene TSHZ3 encoding Teashirt zinc finger homobox 3, predicted by bioinformatics, and matrix metallopeptidase 2 (MMP2), the key pro-invasive protease overexpressed in gliomas. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and Spearman correlation analysis were used to determine differential expressions of miR-338-5p and TSHZ3 in astrocytic gliomas of different grades (n = 35) and glioblastoma cell lines (U87 and U251) in comparison to non-neoplastic brain (NNB) tissues (n = 6). Western blotting was used to determine the protein levels of TSHZ3 and MMP2 in glioblastoma cell lines and Matrigel invasion assay to examine the role of miR-338-5p in cell invasiveness. The results demonstrated that the expression of miR-338-5p, normalized to hsnRNA U6, was significantly higher in grade III and IV gliomas and glioblastoma cell lines in contrast to that in NNB and grade II gliomas, whereas TSHZ3 expression, normalized to GAPDH, was inversely related to miR-338-5p (R = -0.636, P < 0.01). Luciferase assays showed TSHZ3 to be a target gene of miR-338-5p. In both U87 and U251 cells, miR-338-5p mimics increased MMP2 and invasiveness of the cells. Overexpression of ectopic TSHZ3 suppressed the cell invasiveness and attenuated the pro-invasive effect of miR-338-5p mimics. Overall, our results showed that miR-338-5p has a function in promoting glioma cell invasion by targeting TSHZ3 suppression on MMP2. In conclusion, miR-338-5p is a possible potential biomarker for the diagnosis and target for therapy of high-grade glioma[218].
This intricate insight has resulted in not only treating tumours, utilizing ECV’s , but intricate knowledge of molecular modes like MMPs with micro RNA interaction might aid in developing therapies by delivering ECV’s from particular microRNA implicatedin the pathogenesis of diseasesin obstetrics like preeclampsia ,IUGR,besides lot of malignancies like glioblastoma multiforme[[219]. Further Yohan et al showed how targeting the MMP-14/MMP-2/integrin αvβ3 axis with multispecific N-TIMP2–based antagonistsmight be utilized for cancer therapythus utilizing the newer MMP-14or membrane type 1(MT-1-MMP) axis [220]..