Samet Benli1*, Atika Çağlar1, Zeynep Hüz2, Mustafa Aydın1
1Fırat University Hospital, Neonatology Clinic, Elazig/TURKEY
2Fırat University Hospital, Clinic of Pediatrics, Elazig/TURKEY
*Corresponding Author: Samet Benli, Fırat University Hospital, Clinic of Neonatology, Elazig/TURKEY.
Received: July 13, 2023
Accepted: July 21, 2023
Published: July 27, 2023
Citation: Samet Benli, Atika Çağlar, Zeynep Hüz, Mustafa Aydın (2023). “A Case of Idıopatıc Congenıtal Chılotherax in A Premature Newborn”, J Pediatrics and Child Health Issues, 4(1); DOI: http;//doi.org/07.2022/1.1054.
Copyright: © 2023 Samet Benli. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Chylothorax is defined as the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the pleural space and occurs due to congenital and acquired reasons. Although the etiology of congenital chylothorax is not fully understood, it is thought to be the result of a developmental disorder of the lymphatic system. Some patients are asymptomatic or clinically present with mild respiratory distress, while most cases present with potentially life-threatening respiratory distress if left untreated. Conservative and surgical methods are used in the treatment of chylothorax. Conservative approach includes treatment of the underlying disease, repeated thoracentesis or thoracic tube drainage, total parenteral nutrition with interruption of enteral nutrition, and diet containing medium chain triglycerides. The prognosis in chylothorax varies according to the underlying etiology. With appropriate treatment, the prognosis of congenital chylothorax is generally good. However, the degree of accompanying pulmonary hypoplasia, prematurity and presence of hydrops have been reported as causes that increase mortality.
chylothorax; newborn; pleural effusion; respiratory distress
Introduction
Congenital chylothorax in newborns is a serious problem. Congenital chylothorax is defined by the accumulation of abnormal chylous fluid in the pleural cavity and is considered a rare cause of respiratory distress (1). Its incidence is twice as high in males and is seen in 1/10000 infants (2). It is associated with syndromes such as Down syndrome, Noonan syndrome, Turner. However, mostly the underlying pathology cannot be detected and it is defined as idiopathic congenital chylothorax. In the etiology of acquired chylothorax, it usually develops secondary to thoracic duct injury after cardiac (congenital heart diseases) or thoracic surgery (congenital diaphragmatic hernia) in newborns (3). Diagnosis is based on the evaluation of pleural fluid, but is first diagnosed by postnatal direct X-ray or prenatal ultrasonography. Thoracentesis is required for definitive diagnosis. While the fluid taken by thoracentesis in the first postnatal days contains clear and abundant lymphocytes; After feeding, the liquid becomes cloudy and takes on a chylous character. The protein content of the pleural fluid is equal to or less than the plasma protein and tends to collect again after the first thoracentesis. In the treatment, surgical intervention is performed in cases unresponsive to conservative treatment (4). In our article, we wanted to discuss a postnatal idiopathic congenital chylothorax case in a patient followed up for prematurity in the light of the literature.
Case Report
The patient, who was born 750 grams at 27 weeks of gestation from the second pregnancy of a 27-year-old mother, was hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit due to prematurity and respiratory distress. The patient was intubated and surfactant was administered by endotracheal route when the direct chest X-ray showed signs of respiratory distress syndrome. On the postnatal third day, due to decreased aeration of the right lung by listening and a hyperdense image on direct graphy, thoracic ultrasonography was performed and pleural effusion was detected (Figure 1). After thoracentesis performed for differential diagnosis, it was observed that the patient's pleural fluid was white and clear (Figure 2). The density of the pleural fluid was 1015 and the pH was 7.8. In the cell count, 4250 leukocytes/mm³ (92% lymphocytes) were detected. In the pleural fluid, protein was found to be 4.2 g/dl, glucose 165 mg/dl, and triglyceride 1896 mg/dl. Gram stain was unremarkable. There was no growth in pleural fluid culture. His echocardiography did not reveal any pathological findings other than minimal peripheral pulmonary stenosis. Complete blood count examination revealed hemoglobin 14g/dl, hematocrit 52%, leukocyte 17,420/mm3, 54% neutrophils and 46% lymphocytes in peripheral formula. Complete urinalysis was normal. Plasma urea, uric acid, creatinine, electrolyte values, cholesterol, triglyceride, blood sugar values are within normal limits; serum albumin was 3.2 g/dl. No pathology was detected in chromosome analysis, metabolic scans and TORCH scan. In our patient; Congenital chylothorax was diagnosed because clinical and laboratory findings were compatible with chylothorax and there was no risk factor in the postnatal period in the differential diagnosis. Our patient died on the postnatal seventh day due to respiratory distress.
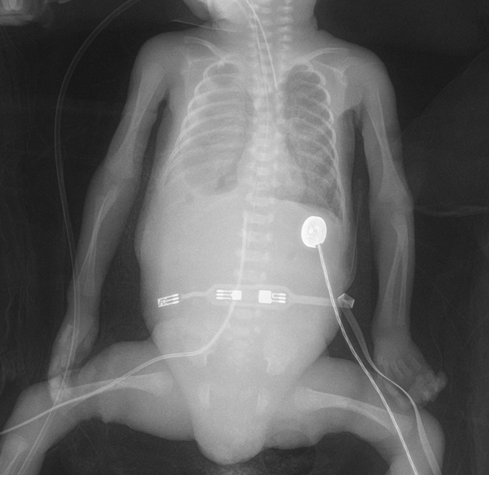
Figure 1. The chylothorax image of the patient at the base of the right lung on the direct radiograph
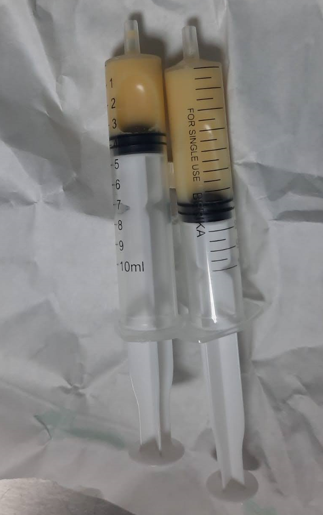
Figure 2. Image of chylous fluid
Discussion
Congenital chylothorax was first reported in the 17th century and is rare. It is a common cause of neonatal pleural effusion. Trauma and postcardiothoracic surgery are accepted as causes in etiology, but it is generally associated with lymphatic malformation such as lymphangiectasia in newborns, congenital cytomegalovirus, adenovirus, streptococcal infections, aneuploidy syndromes such as congenital goiter, Turner and Down syndrome, Noonan syndrome and malignancies (5,6).
The characteristics of pleural chylous fluid are as follows: triglyceride >100 mg/dl, protein >20 g/L, lymphocytosis >100 cells/ml, cholesterol 65-220 mg/dl. High triglyceride level and low cholesterol level distinguish true chylothorax from pseudochylothorax. The pleural fluid in culture is sterile (7). Laboratory findings of our patient were similar. Congenital chylothorax is associated with high morbidity and mortality (50%), especially in preterm and low birth weight infants. A small number of cases show spontaneous resolution (8).
There is no consensus on the treatment approach to chylothorax, but conservative treatment with infection control, nutrition and fluid electrolyte management and respiratory support is the common treatment. Surgical pleurodesis, thoracic duct ligation should be performed in resistant cases with excessively prolonged (3 to 4 weeks) drainage or collection >10 ml/kg/day and recurrent chylothorax. These procedures have their own complications and disadvantages as in different studies (9,10). A more conservative approach, such as octreotide infusion therapy, has had some success in the treatment of chylothorax (11). The mechanism of action of somatostatin in chylothorax is not clearly known. However, it has an antisecretory effect by reducing mild splanchnic vasoconstriction and all gastrointestinal-pancreatic secretions, intestinal absorption and hepatic venous flow. Octreotide is usually started with a slow infusion of 0.5-1 mcg/kg/hr and gradually increased until the desired effect. The normal dose range is between 0.2-10 mcg/kg/hour. In a study conducted on neonatal chylothorax, they found that the average for maximum antisecretory effect was 3 days from the start of treatment (12). As side effects of octreotide, hyperglycemia / hypoglycemia, gallbladder sludge, cardiac conduction disorder, hormone antagonism (cortisol, insulin, glucagon, thyroxine, etc.) can be observed (13). It is relatively free of side effects in newborns, but caution should be exercised in infants with NEC. Ocreotide treatment was not planned in our patient because chylous fluid did not come out after thoracentesis.
In conclusion, congenital chylothorax is a rare but serious condition in newborns. Early diagnosis and intervention in the prenatal period supports the improvement of postnatal outcomes. Postpartum management includes drainage of pleural fluid, dietary changes, medication, and rarely surgery. In this case, there is no universally accepted guideline for the use of drugs and the duration of conservative treatment. Generally, the outcome of the condition depends on the underlying genetic condition and associated malformations.