Neurosurgery and Neurology Research
OPEN ACCESS | Volume 7 - Issue 1 - 2025
ISSN No: 2836-2829 | Journal DOI: 10.61148/2836-2829/NNR
Bafandegan Vahid.
Department clinical psychology, Neyshabur University, Iran
Corresponding author: Bafandegan Vahid, Department clinical psychology, Neyshabur University, Iran
Bafandegan Vahid.
Department clinical psychology, Neyshabur University, Iran
Corresponding author: Bafandegan Vahid, Department clinical psychology, Neyshabur University, Iran
Received date: December 23, 2020; Accepted date: December 20, 2020; published date: December 29, 2020
Citation: Vahid B. “The predicted role of parenting styles in man treated for substance abuse”. J Neurosurgery and Neurology Research, 1(1); DOI: http;//doi.org/03.2020/1.1003.
Copyright: © 2020 Bafandegan Vahid. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This study aimed to investigate the predicted role of parenting styles in man treated for substance abuse. This investigation was descriptive prediction, which using convenience sampling was performed. 200 men treated for substance abuse. The tool for dada collection was baumrind parenting style questionnaire (1972), that the participants in the study completed it. Result indicated that parenting styles are significantly associated with substance abuse and permissive and authoritarian parenting style were positive predictor for tendency to drug abuse according to this findings and in link with the research literature, we can conclude that the drug dependent patients more likely to belong to families with dysfunctional parenting styles and be emphasize the importance of family institution in tendency to substance abuse. This topic in countries with religious dictatorships such as Iran-Due to the crisis of addiction and depression-Is predictable.
Introduction
Each person's lifestyle, behaviour, and personality are a direct and indirect reflection of their family and social environment throughout their lives and the family is the main and important centre of society and the dominant atmosphere in the relationships within it, plays an important role in people's health. The importance of family-related processes in the development of family members has been considered by psychologists. Baumrind (1966) proposed three different qualitative styles for parenting that have different health-related implications: Authoritative parenting, authoritarian parenting and permissive parenting.
For more than fifty years there have been hundreds of studies examining the efficacy of her model. In 1983, Maccoby and Martin expanded her model to include a fourth parenting style called Rejecting-neglecting, an uninvolved parenting style. Parental Demandingness and Responsiveness...
In one parenting style, parents are demanding and not accountable; in a parenting style, parents are both demanding and accountable (Kramer, 2011). People who are addicted to drugs are more likely than other people to belong to families with poor functioning characteristics and unhealthy structure. Poor relationship quality, Lack of clear rules, More or less involved in children's affairs, Lack of parental coordination in applying the rules and Poor parental control over children's activities can be a risk factor for behavioural problems and substance abuse in children. (Talib, J.Mohamad, Z.Mamat, M, 2011). There is a relationship between parenting styles and relationships within the family with addiction, So that rejection and lack of warm and emotional relationships among the families of addicts is very high (Feizi, M., Gholami, M., Poosti, A., Mayvan, F. A., Kamali, Z., & Toghraee, M, 2019). Based on research by Yu and Steve Mann (2010) Negative family relationships have directly and positively predicted drug abuse among American-Indian people. On the other hand, socially weak sections of society are more exposed to psychological harm than other citizens. In Iran, refugees, the unemployed, the homeless, children and adolescents and War-torn areas are considered vulnerable groups. In Iran, according to Khamenei's leadership as a dictator of Shiite Islam, the range of types of violence, such as executions, is very wide and no one is safe from the consequences and this religious determinism extends to subordinates from the highest levels of government to the smallest components of society, such as families and parents (Deusche welle 2012.02.24). A clear example of religious determinism can be found in the study of Adibi and Rezaei (2018), they came to this conclusion: The parents of military children (sepah pastaran) are more inflexible than other social groups and children have higher levels of depression and addiction. Given what has been said, the aim of this study was to determine the extent of parenting styles in predicting substance abuse among addicts.
Methodology
The present study is descriptive and predictive .The statistical population included all men undergoing drug abuse treatment in Mashhad. The sample was selected from drug treatment centres, Available sampling method was selected from four substance abuse treatment centres- 200 men between the ages of 25 and 35 were selected.
Instrument
Parents parenting styles scale. This questionnaire was designed by Diana baumriand in 1972 and it includes 30 items which evaluates three parenting styles as: authoritative, authoritarian and permissive styles. The questions responding pattern follows a 5 degrees Likert scale from I totally agree "to" I totally disagree Boory in 1991 reported the mentioned questionnaire reliability by using retest method between mothers 0.81 for permissive style, 0.86 for authoritarian style 0.78 for authoritative style and between fathers 0.77 for permissive style, 0.85 for authoritarian style and 0.88 for authoritative style respectively. Moreover, Esphandiari (1374) also reported test reliability in a retest method and in a one week interval on a sample of 12 mothers for permissive style (0.69) authoritarian style (0.77), and decisive and assuring style (0.73) respectively (Malkpour, 2002). After completing the questionnaire by the mothers, the obtained information was analysed by using descriptive and perceptive statistical methods as independent t-test groups and two-way variance (ANOVAs) analysis.
Finding
Results of regression coefficient showed: There was a positive and significant correlation between permissive and authoritarian parenting style and substance abuse. While there was no negative but significant correlation between authoritative parenting style and substance abuse.
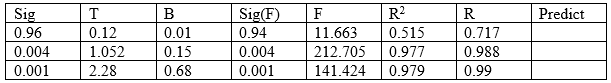
Table1. Results of regression coefficient analysis based on two variables
Conclusion
Substance abuse and addiction are a social and medical problem today and includes biological, psychological, social, cultural and political dimensions. Sixty percent of Iranian prisoners are in prison for drug-related crimes Razzaghi, E., Rahimi, A., Hosseini, M., & Chatterjee, A. (1999(This study aimed to investigate The predicted role of parenting styles in man treated for substance abuse. Based on the data obtained from Table 1: it was a positive and significant correlation between permissive and authoritarian parenting style and substance abuse. While there was no negative but significant correlation between authoritative parenting style and substance abuse. Findings of the study are consistent with the study of Ahmadi, V., Ahmadi, S., Dadfar, R., Nasrolahi, A., Abedini, S., & Azar-Abdar, T. (2014( which indicates the effectiveness of authoritative parenting style in reducing addiction and the inefficiency of authoritarian style in terms of increasing addiction in children. Given that pre-addiction is prepared, parenting styles can play a mediating role in this regard. In addition, the possibility of intergenerational transmission of abuse in addicted families due to rejection and aversion to the family is high. Therefore, teaching parenting styles and the consequences of each on the behaviour and personality of children is one of the preventive measures to reduce the number of drug addicts. One of the limitations of the present study: Reduce the power of generalizability or low control over research variables. Therefore, it is not possible to Causal inference from these findings.