Maeda K 1, Utsu M 2, Serizawa M 3.
1 Honorary Prof. ObGyn, Tottori University Medical School, Yonago, Japan
2 Department of bstetrics and Gynecology, Seirei Mikatahara hospital, Hamamatsu, Japan, and
3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Hamamatsu Medical center, Hamamatsu, Japan.
*Corresponding author: Maeda K, Honorary Prof. ObGyn, Tottori University Medical School, Yonago, Japan.
Received: January 03, 2021
Accepted: January 11, 2021
Published: January 18, 2021
Citation: Maeda K, Utsu M, Serizawa M. “Fetus is Mature at Braxton-Hicks Sign after 32 Weeks of Pregnancy”. International Journal of Clinical Gynaecology and Obstetrics, 2(1); DOI: http;//doi.org/03.2021/1.1004.
Copyright: © 2021 Maeda K. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Aims: Fetal maturity was estimated by various methods in 164 mono- chorionic diamniotic (MD) twins.
Methods: Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) was prevented by intensive maternal rest and tocolysis until fetal adrenal cortex maturity, which was estimated in the initiation2mechanism of uterine contraction, gray level histogram width (GLHW) of fetal lung and liver ratio multiplied by gestational weeks was used to estimate fetal lung maturity.
Results and discussion: Fetal adreno-cortical steroid, reacted stresses after maturation, which caused Braxton-Hicks uterine contraction at 32 gestational weeks, where ultrasonic cardio-thorax ratio enlarged to 0.4 or more, then the MD twins received cesarean delivery to prevent TTTS in 32±2.2 gestational weeks where coefficient of variation (CV) of weeks was as small as 7 %, less than 10%, thus, fetal maturity was estimated to be 32 gestational weeks. As GLHW ratio of fetal lung and liver multiplied by gestational weeks was > 29, which meant mature fetal lung, the index was 32 gestational weeks, and there was no problem in the MD twins born in 32±2.2 gestational weeks.
Conclusion: Fetus is mature at Braxton-Hicks sign which was 32 gestational weeks.
Methods
We would like to confirm fetal maturation in the management of 164 MD twins born by cesarean delivery after the maternal rest, tocolysis and detailed ultrasound studies, developed no TTTS in the MD twins, while the existence of mild blood transfer to the recipient twin from the donor, was detected by larger CTR than 0.4, fpllowed by cesarean section. .
Fetal lung gray level histogram width (GLHW), that is an ultrasonic tissue characterization, was measured in fetal lung and liver to estimate the lung maturity (figure 1) [1], and the fetal age was studied in Braxton- Hicks uterine contraction, which determined the cesarean delivery at 32±2.2 gestational weeks.
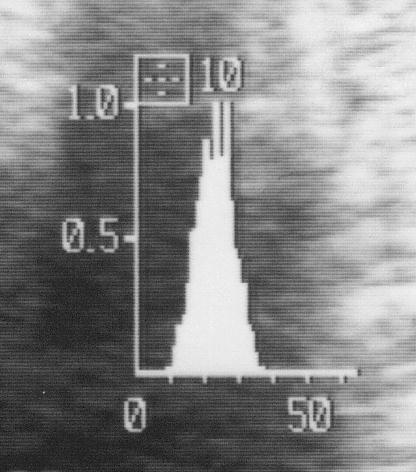
Figure 1: GLHW calculation in common echodencity histogram. A/B (%) is GLHW. It is automatically achieved by ”%W” index in the histogram of Aloka B-mode device [3].
Results
Fetal lung GLHW was 35 and that of fetal liver was 36 in 32 weeks of pregnancy [2]. Fetal lung was mature, because the lung/liver ratio of GLHW multiplied by pregnancy weeks was 31 which was larger than 29 in 32 weeks of pregnancy [2], when the twins received cesarean delivery to prevent TTTS after the first blood transfer to recipient from the donor, which was suspected to be caused by a Braxton Hicks uterine contraction. Although there was very mild reactive cardiac function change in the recipient only within 2 days in the NICU, the infants were healthy and no failure afterwards.
Novel treatment of MD twins to prevnt TTTS was beneficial because the MD twins received cesarean delivery after ultrasonic imaging of CTR larger than 0.4, which was resulted by the inflow of blood into the recipient heart in the uncontrollable uterine contraction, which was uncontrollable by maternal rest and tocolysis in around 32 gestational weeks, which would be Braxton-Hicks contraction caused by prostaglandin developed at placental site by the emission of fetal adrenal corticosteroids against various stresses. In summary, the uncontrollable uterine contraction might be a Braxton Hicks contraction, which was caused by fetal reaction to the stress around 32 weeks, where it is a physiologic and endocrine reaction of a mature fetus to the stress. Therefore, it was uncontrollable by the tocolysis with terbutaline.
Discussion
The 82 mothers of 164 MD twins who received the treatments with maternal rest and tocolysis followed by cesarean delivery at around 32 weeks of pregnancy. Why there was no TTTS in pregnan- cy ? The early TTTS might develop by blood transfer in no ultrasound monitoring in the pregnancy, and controllable contraction was suppressed by maternal rest and tocolysis in our novel treatment. The 32 weeks of pregnancy will be important fetal age in our present study, namely, it may indicate the time of fetal maturity, as the 32 weeks of pregnancy is the stage when transient Braxton-Hicks’ contraction initiates before the appearance of labor contraction. According to approved theory, the fetus excretes adrenal cortico- steroids into umbilical blood flow which reaches placenta, stimulating local decidua to secrete prostaglandin developing the initial uterine contraction at placental site as the pace-maker of whole uterine contraction, namely, the Braxton-Hicks contraction may show the fetal maturity in the production of protective adrenal corticosteroid against stresses. If so, the authors would keep the pregnancy until the stage of the functional maturity of twins to resist stresses. The Braxton-Hicks contraction will enhance the first blood transfer to the recipient from the donor and enlarged the recipient heart in MD twins. Thus, the twins were guarded by fetal functional maturity from the cesarean delivery, where the cesarean delivery would not damage twins. Also, there was no problem in the infants after the cesarean delivery. The Braxton-Hicks contraction may promote the blood transfer, but there was the interval to prepare the cesarean delivery. Also, the Brasxton-Hicks contraction would be uncontrollable by the tocolysis, because it was physiologic and endocrinologic,
Conclusion
Fetal functional maturity will develop at around at 32 weeks of pregnancy, which was estimated by fetal lung maturity and Braxton-Hicks uterine contraction.