Clinical Case Reports and Clinical Study
OPEN ACCESS | Volume 13 - Issue 1 - 2026
ISSN No: 2766-8614 | Journal DOI: 10.61148/2766-8614/JCCRCS
T. Meghana and Abbaraju Krishna Sailaja*
Department of pharmaceutics, RBVRR women’s college of pharmacy, Affiliated to Osmania University, Hyderabad, 500036
*Corresponding author: Abbaraju Krishna Sailaja, Department of pharmaceutics, RBVRR women’s college of pharmacy, Affiliated to Osmania University, Hyderabad, 500036.
Received: December 01, 2021
Accepted: December 13, 2021
Published: December 18, 2021
Citation: T. Meghana and Abbaraju Krishna Sailaja “Herbal Antifungal Agents Used for The Treatment of Fungal Infections.” Clinical Case Reports and Clinical Study, 5(4); DOI: 10.61148/2766-8614/JCCRCS/096
Copyright: © 2021 Abbaraju Krishna Sailaja. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Now a days, fungal infections of skin is one of the most common dermatological problems in world wide. It has been investigated that 40 million people suffer from fungal infections. Fungal diseases are infections caused by a fungus, a type of microorganism. Most commonly used antifungal drugs such as amphotericin B and other drugs like ketoconazole, fluconazole and clotrimazole are limited in their spectrum and may produce strain resistances. Major antifungal treatments have various drawbacks in terms of toxicity, efficacy as well as cost. Antifungal agents used clinically to treat fungal infections i.e., azoles, allylamines, griseofulvin. The review focus on the use of herbal treatment for fungal infections because herbal plants have less toxicity and no limits of treatment while synthetic treatment have limited criteria.
Introduction:
Fungal infections are one of the deadliest infections accounting in excess of 1.5 million deaths annually worldwide. The main reason for fungal infection is neglected by the society. Over the past two decades, fungal infections have increased significantly in frequency and as causes of morbidity and mortality.
Fungal infections are also called mycosis, is a skin disease caused by a fungus and a type of microorganisms. There are millions of species of fungi, fungi can live in the air, soil, water, plants and also live-in human body. They can also lead to skin problems like rashes or bumps. Fungal infections come in different forms like ringworm, athletes’ foot, yeast infections and jock itch. Some fungi like aspergillus can be dangerous and leads to life threatening disease. Fungal infections can be contagious and can be spread from one person to another person.
COMMON SYMPTOMS INCLUDES:
ADVANTAGES OF TROPICAL TREATMENT FOR FUNGAL INFECTIONS:
TYPES OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS:
Ringworm is a common fungal skin infection and is highly contagious. It is caused by a fungus and not by a worm. Sometimes it can be found on the scalp.
SYMPTOMS:
It is a fungal infection that affects the skin on your feet and between your toes. This infection can spread to other area of the body like nails, groin or hands.
SYMPTOMS:
It is a fungal skin infection that occurs in the area of groin and thighs. It is caused by fungus that can be spread from person to person. It is mostly seen in men and adolescent boys.
SYMPTOMS:
It is a fungal infection affects the skin of scalp and hair shafts. It is most common in young children.
SYMPTOMS:
It is a fungal/ yeast skin infection that causes small discoloured patches to show up on the skin. It is most common in adults. This discoloured skin patches occurs on the back, chest and upper arms. It mostly occurs in summer or wet climate
SYMPTOMS:
It is a skin infection caused by candida fungi. It is naturally present inside the body. It occurs in areas thar are warm, moist and poorly ventilated.
SYMPTOMS:
HERBAL REMEDIES TO TREAT FUNGAL INFECTIONS:
HERBAL PLANTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS:
|
SCIENTIFIC NAME |
LOCAL NAME |
FAMILY |
USES |
|
Azadirachta indica |
Neem |
Meliaceae |
Antifungal, antimalarial, antiviral, antioxidant and also used in ulcers and eczema |
|
Allium sativum |
garlic |
Liliaceae |
Used as rubefacient in skin disease, used in treatment of atonic dyspepsia |
|
Ocimum sanctum linn |
Tulsi |
Labiaceae |
Fresh leaves bruised and applied externally for curing ringworm and skin diseases |
|
Coccinia indica |
Ivy gourd |
cucurbitaceae |
Used for ringworm, psoriasis, smallpox, scabies and ulcers |
|
Datura metel |
Datura |
solanaceae |
Used as antimicrobial activity and antifungal activity |
|
Moringa olifera |
Sajina |
Moringaceae |
Used as purgative and for cough |
|
Psidium guajava |
peyara |
Myrtaceae |
Used as a gargle for mouth wash in swollen gum and locally applied to the ulcers |
HERBAL ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS:
Many of the pharmaceuticals presently available have a long history of use as herbal remedies including opium, aspirin, digitalis and quinine while their purification and quantification makes them more predictable. Herbal remedies tend to have a more complex and subtle mix of chemicals and can sometimes can offer access the drugs that the pharmaceutical industry has not yet exploited. Some of the antifungal drugs most recently introduced are derived from natural products which has showed good effect to the individuals with fungal infections. There is a need to develop more antifungal agents with lesser side effects, fewer dose limiting and which are economic. Herbal formulations always have attracted considerable attention due to their good activity and comparatively lesser side effects when compared to synthetic drugs.
MARKETED PREPARATION:
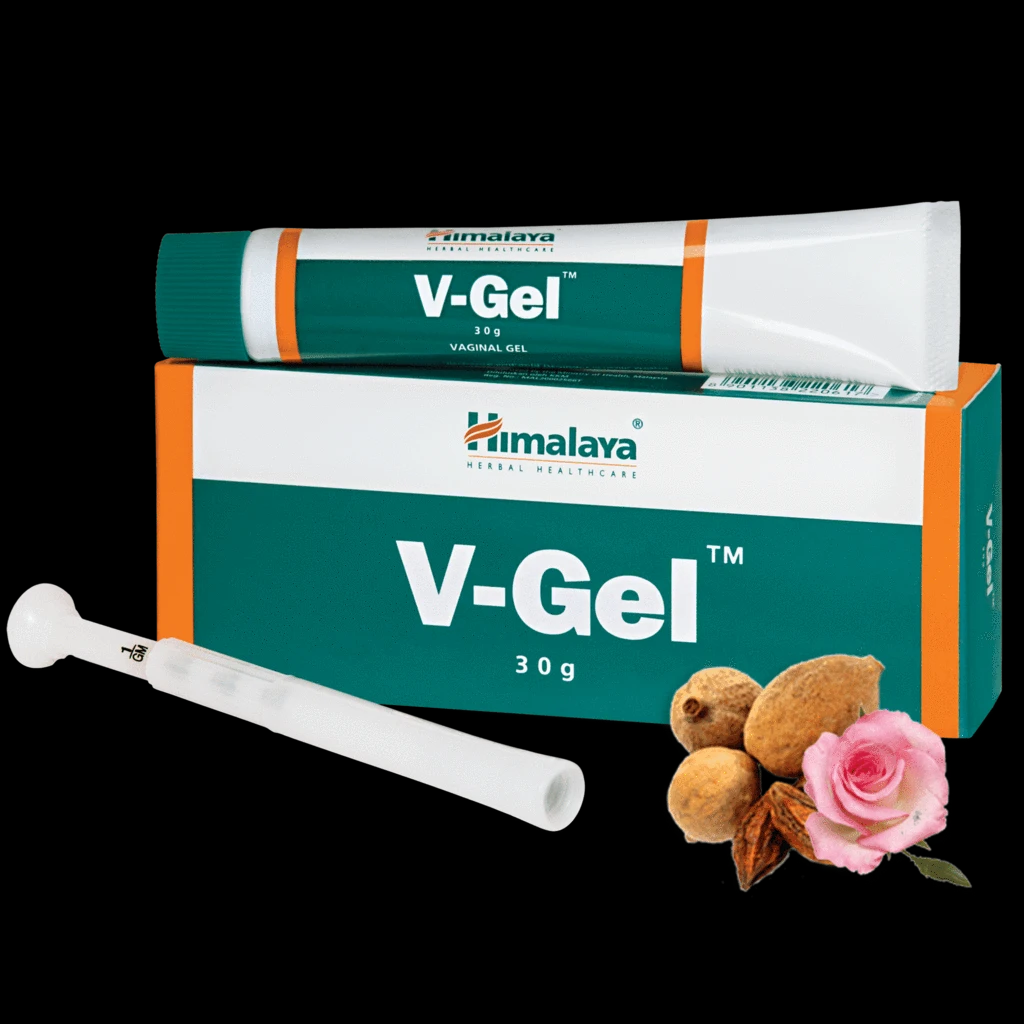
Himalaya V-gel: Himalaya V-gel consists of Persian rose, triphala and cardamom. Himalaya V-gel is indicated for vaginal candidiasis (fungal yeast infection), vaginal trichomoniasis (parasitic vaginal infection) and nonspecific bacterial vaginitis.
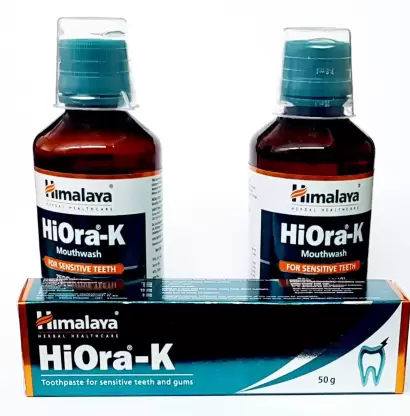
HIMALAYA HIORA MOUTH WASH: It kills germs, tones gums and refreshes mouth. It contains meswak, beteland bibhitaki. Belleric myrobalan (Bibhitaki) is an antimicrobial and antifungal agent that keeps infections away.
CONCLUSION:
The last 20 years has shown an increase in number of fungal infections. Presently worn drugs in treatment of fungal infections are having many side effects and development of resistance is very common against these drugs. Plants have been considered as traditional source of antifungal medicines for past many years. Plant bioactive with antifungal activity can be contemplate as an option for development of new and improved backup formulations in antifungal therapy. Development of improved formulations with plant phytocompounds is the need of the hour for efficient treatment of fungal diseases. Further research on this field can provide us with increased number of options in treatment of fungal diseases that will give the patients with a better quality of life.